Healthy radiant skin with an impeccably even relief and uniform color is the key to the beauty and success of its owner, regardless of gender. With age or as a result of trauma, as well as exposure to other pathological factors, negative changes occur in the tissue composition of the dermis: the surface and deeper layers are thinner, the volume and amount of elastic fibers are reduced, causing skin atrophy processes.
Appearing on open areas of the human body (face, décolleté, collar, hands and other surfaces), these aesthetic imperfections spoil the overall impression of the exterior. Often they cause the majority of women and men not only physical as moral suffering. Immediate medical attention and adequate treatment will help to avoid irreversible pathological changes in the dermis.
Classification
Doctors distinguish between physiological (or natural) destruction of the skin, resulting from the gradual aging of the body, and pathological, in which not all skin is affected, but its individual parts. After fifty years of age or physiological atrophy of the skin, it is associated with changes in the hormonal sphere, the blood supply system of tissues, the chemical composition of the blood, and also with impaired neurohumoral regulation of the physiological functions of the body.
This process develops slowly and gradually over many years. Several signs of division are inherent in the pathological destruction of the skin: by the nature of the formation (primary and secondary); by prevalence (diffuse and limited); by the time of appearance (congenital and acquired).
Primary atrophy of the skin (the photo of which shows the presence of stretch marks, or striae) is due to pregnancy, when there are significant changes in the work of the endocrine organs.
With diffuse damage to the skin, an impressive part of the surface changes, including the outer layer of the epidermis of the hands and feet. A limited form of the disease is characterized by the presence of local foci adjacent to unchanged healthy skin.
Secondary destruction of the dermis occurs in parts of the body previously affected by other diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis, lupus erythematosus and other inflammatory processes or skin disorders - companions of diabetes mellitus).
Local skin atrophy after hormonal ointments most often occurs in children, young women or adolescents with the uncontrolled use of drugs, especially those containing fluorine (Sinalar or Fluorocort), as well as the increased effect of ointments prescribed for use under an occlusive (hermetic) dressing.
Etiological factors of development
The most common form of damage to the structure of the skin is hormonal atrophy of the skin that occurs during pregnancy or with obesity associated with metabolic disorders. During stretching or breaking of elastic fibers, striae appear in various parts of the body.
Other triggers of this skin ailment are:
- endocrine disorders (including Itsenko-Cushing's disease);
- malfunctioning of the central nervous system;
- eating disorders (including malnutrition);
- rheumatic diseases;
- infectious lesions (tuberculosis or leprosy);
- exposure to radiation and burns;
- traumatic injuries;
- dermatological diseases (lichen planus, poikiloderma), as well as the use of drugs containing glucocorticosteroids (including in the form of ointments).
Despite the many provoking factors, the basis of the appearance of skin atrophy is laid down the mechanism of local biodegradation of tissues, in which their nutrition is disturbed, and the activity of skin cell enzymes is significantly reduced. This leads to the predominance of the processes of catabolism (destruction of the structure of tissues) over anabolism (their construction or restoration).
Signs by which to identify foci of the disease
The peculiarity of degenerative tissue changes due to skin atrophy is associated with thinning of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, the appearance of translucent vessels and age spots, telangiectasias (spider veins) or malignant neoplasms. Simultaneously with a decrease in the volume of the dermis, local compaction of the skin due to the proliferation of connective tissue can be noted. Changed areas of the disease are often localized in the face, chest, abdomen, lower back and hips. Outwardly, they are hollows of the skin covered with a thin whitish dermis resembling tracing paper (or tissue paper).
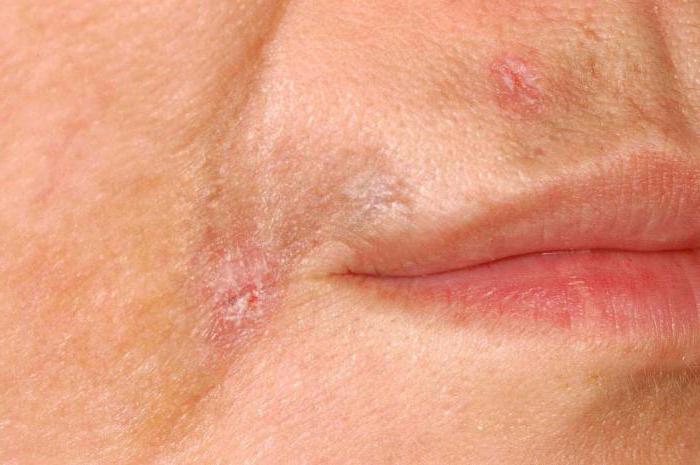
Cosmetic defects in the form of sunken “islands” with various shades: from pearly white to blue-red or venous nets, can coexist with healthy areas of the skin. Violation of metabolic processes in the dermis leads to the appearance of folds with thinned skin, any careless touch to which can damage the epidermis. In elderly patients, stellate pseudo-hems, hemorrhages or hematomas often occur in the affected area .
What doctors are needed for diagnosis and treatment
Pathological atrophy of the skin, the treatment of which is a whole complex of various measures, should be examined by many specialists. To confirm or exclude this diagnosis can dermatologists with the involvement of endocrinologists and neuropathologists, allergologists and infectious disease specialists, surgeons and oncologists. Scars below the skin level that result from injuries or medical procedures, burns, chickenpox or acne should be shown first to a dermatologist.
The treatment method for professionals
The methods for treating this disease depend on a number of factors: the etiology and localization of the destructive process, age, state of health and patient persistence. Skin atrophy after hormonal preparations (including the use of external agents in the form of ointments) can occur a long time (up to several months!) After the endocrinologist completes treatment.
In order to activate the process of tissue repair, it is necessary at the initial stage to cancel taking drugs containing corticosteroids. With secondary pathology of the dermis, the doctor recommends initially curing the underlying (previous) disease, and then proceed to improve tissue trophism, saturate the body with vitamins, and in some cases, use antibiotic therapy.
When is the surgeon's help needed? It is needed to excise small atrophic scars, with multiple or large boils, carbuncles, deep purulent processes in the tissues, as well as for skin transplantation. An oncologist consultation is necessary if various neoplasms appear on the surface of the foci (warts, papillomas, and others). With the help of a biopsy, the nature of the growths is determined to prevent the occurrence of oncological problems.
Procedures
Modern medicine has many different methods for getting rid of an unaesthetic defect, such as atrophy of the skin of the face or any other area of the dermis. The arsenal of professionals includes:
- surgical excision of the lesion;
- mesotherapy;
- microdermabrasion;
- laser therapy;
- chemical peeling;
- subcision or undercutting of scars;
- cryotherapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- enzyme therapy;
- hydration;
- treatment with special creams and ointments.
Depending on the degree of the disease, its etiology, age of the patient and the presence of chronic ailments, the clinic specialist selects the optimal set of procedures.
The standard treatment regimen includes: taking multivitamin complexes that stimulate the immune and regenerative processes in the patient's body; physiotherapeutic procedures that promote activation of blood supply to the affected areas of the dermis, as well as injections or taking Pentoxifylline (the commercial name is Trental), which improves blood microcirculation.
At the clinic of aesthetic surgery
Considering the various methods of treating this ailment, to achieve an optimal result, a dermatologist can recommend the correction of scars surgically to make them as accurate and invisible as possible. For this purpose, a laser or scalpel is used, which raises the edges of the affected area or transplants the skin from healthy areas.
Another method is subcision. It involves cutting and raising the connective fibers produced by the body at the site of the scar, using a special needle. Raising the bottom of the focus, the needle releases it, aligning the damaged surface of the dermis.
Other methods:
- microdermabrasion (skin resurfacing with microscopic crystals);
- mesotherapy (injections of therapeutic cocktails into the middle layer of the skin to stimulate the synthesis of collagen fibers, correct scars and age-related atrophic changes);
- chemical peeling (with removal of the upper layers of the skin - from the superficial keratinized, to the median and deep);
- enzyme therapy;
- hydration (with hyaluronic acid-based preparations);
- laser therapy.
Methods can be used both for the correction of scars and for improving the appearance of the skin during aging.
Ointments
Hardware methods of treating destructive processes in tissues can be practiced in combination with the use of external agents. How is the right ointment selected? Skin atrophies are dermal diseases that should be treated exclusively by a specialist! Self-treatment of scars and pathologically changed areas of the dermis can lead to a deterioration in their appearance and condition.
To solve an individual aesthetic problem, the doctor prescribes gels and ointments that improve blood circulation in tissues, their nutrition and oxygenation, have anti-inflammatory and stimulating tissue regeneration properties: Contractubex, Kelofibrase, Stratoderm, MedGel, Dermatix, Scarguard and Kelo-cote, choosing the most suitable drug .
Traditional medicine in the fight against destructive skin changes
Treatment of skin atrophy with the help of home baths, lotions and healing oils, taking tinctures, decoctions and infusions from medicinal plants is allowed with the permission of the doctor in combination with traditional methods. For example, when the initial signs of white atrophy appear (small foci of round or irregular shape in the color of white porcelain), herbalists advise chopping chestnut fruits (100 g) and pour 0.5-0.6 l of alcohol into them. Insist the remedy for a week in a place closed from light rays. Take chestnut tincture inside 10 drops 3 times a day. A similar homemade nutmeg medicine (prepared in the same way) is consumed in 20 drops with the same frequency.
External folk remedies for skin ailment
Powder from dried leaves (string, yarrow, thyme, birch buds and eucalyptus) is diluted in almond and peach oils taken in equal proportions (50 ml each), and one tablespoon of glycerin is added. From skin lesions associated with burns, traditional medicine suggests the use of chamomile flowers, calendula, nettle leaves, yarrow and hypericum sprouts, dried marshmallow and bird mountain. Decoctions for lotions from these herbs can also be used, in the form of a powder mixed in rosehip, sea buckthorn or corn oil. The beneficial effect on the skin is the addition of yellow beeswax to homemade “ointments” with vegetable oils and medicinal herbs.
Prevention and improvement of the appearance of the skin
There are several specific measures to prevent the occurrence of destructive skin changes in adults and children: to carefully use hormonal preparations, avoid prolonged contact with direct ultraviolet rays, monitor the general state of health and skin, and carry out immediate sanitation of the foci of infection in the dermis and in the body as a whole. Atrophy of the skin after hormonal ointments requires the termination of their use and consult a doctor. Regular examination and timely detection of serious diseases (diabetes, dangerous infections, disorders in the hematopoiesis system) will also help to avoid problems with the destruction of the skin structure.

Moisturizing the abdomen during pregnancy with creams, olive oil or gels will prevent the appearance of stretch marks (stretch marks). Skin care and regular visits to the beautician will help rejuvenate and accelerate the regeneration of the dermis. For all types of atrophy, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated for the prevention and elimination of the ailment: sulfur and hydrogen sulfide baths, therapeutic mud, as well as vitamin fortifying therapy.