The spine is our inner skeleton. It performs supporting, motor, cushioning, protective functions. Violation of these functions occurs with spinal deformities. To return them, you need to deal with the prevention and timely treatment of curvature of the spine. The pathologist is engaged in an orthopedist, vertebrologist and neurologist. It all depends on the cause of the curvature and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Normally, it has several bends in each of its departments, which are located in the sagittal plane (if viewed from the side).
Physiological bends of the spinal column
- Cervical and lumbar lordosis. They are formed in the process of the child’s physical development when his motor abilities expand (he begins to hold his head and sit). They are the bulge of the spine anteriorly.
- Thoracic and sacral kyphoses are formed in utero, the baby is already born with them. Represented by a bulge at the back.
In the frontal plane, the line of the spine runs along the mid-axis of the body. Active and proper retention of the body in space is posture. Deformation of the spine leads to the development of pathological posture and vice versa.
Types of disease
What are the types of spinal deformities? What most often bothers modern man? Scoliosis develops in the frontal plane. This is a curvature of the spinal column relative to the median line to the right or left. In the sagittal plane, an increase in the arc of physiological bends (hyperlordosis, hyperkyphosis), disappearance or decrease in bends (flat back), and combined curvatures combining two directions (lordoscoliosis, kyphoscoliosis) are observed.
Why does warping occur?
Causes of spinal deformity can be congenital and acquired. Congenital etiology is associated with vertebral pathology:
- Underdevelopment of structural components.
- Additional elements.
- The fusion of adjacent vertebral bodies.
- Non-arcing.
- Wedge shape.
Reasons for acquired spinal deformity may include:
- Systematically incorrect posture.
- Rickets (the balance of calcium in the body is disturbed, the bones become fragile).
- Tuberculosis of the spine.
- Polio.
- Osteochondrosis and osteodystrophy.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Injuries, hernias and spinal tumors.
- Pleurisy is a pathology of the respiratory system with severe pain. Usually one side is affected on which the patient lies. The load on the spinal column in the thoracic region is uneven, there is a curvature.
- Shortening one of the lower extremities - the load is distributed unevenly.
- The absence of one arm or leg and, as a result, an imbalance.
- Weak muscle mass that is not able to withstand spinal curvature.
- Mental disorders (depression, when the shoulders and head are constantly lowered).
Curvature of the spinal column can affect any part of it.
Deformation of the cervical spine
- Torticollis is a pathology in which at the same time there is a tilt of the head in one direction and a turn of the neck in the other.
- Kyphosis - posterior neck curvature . This is a rare occurrence.
- Lordosis is an increase in physiological bending. The neck is extended forward, shoulders are rounded, stoop develops.
Causes of congenital torticollis:
- improper intrauterine position of the fetus;
- birth injuries;
- spasm or shortening of the neck muscles;
- congenital pathology of the cervical vertebrae (Klippel-Feil disease);
- rotational subluxation of the 1st cervical vertebra.
Causes of acquired deformity of the cervical spine:
- installation torticollis - when the child has been in the wrong position in the crib for a long time;
- compensatory - with inflammatory diseases of the ear, purulent processes in the neck (the child spares the sick side and tilts his head to a healthy one);
- fracture, dislocation or subluxation of the first cervical vertebra;
- osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, tertiary syphilis - vertebrae are destroyed, axial deformation of the skeleton occurs.
Torticollis Treatment
Conservative methods:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- position treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- water procedures in the pool using a circle for newborns;
- wearing a collar that fixes the cervical spine in the correct position.
Surgical treatment is performed in the absence of a conservative effect:
- myotomy - dissection of the neck muscle;
- plastic (muscle lengthening).
Kyphosis and lordosis are treated with conservative methods (exercise therapy, massage, drug anesthesia, muscle spasm relief).
Thoracic Disorders
Kyphosis is accompanied by deformation in the form of increased physiological bending. There is a pathological bending posteriorly with the formation of a round back. Acquired kyphotic spinal deformity is more common.
Causes of breast kyphosis:
- Weakness of the muscle corset, which does not have time to form after the accelerated growth of the child.
- Early rickets (up to 1 year) - the thoracic and lumbar regions are affected. The deformation disappears in a lying position (unfixed curvature). The severity of the pathological bending is aggravated when the child sits down and stands on its feet.
- Late rickets (5-6 years) - fixed kyphoses and kyphoscolioses develop.
- Osteochondropathy is observed at the age of 12-17 years. More often boys suffer. In the medical world it is called Scheuermann-Mau disease. Dystrophic changes develop in the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. A fixed wedge-shaped deformation of the spine is formed.
Treatment of breast kyphosis
Rickety deformity is treated conservatively: swimming, vitamin therapy, exercise therapy, coniferous baths, massage, wearing a special three-point corset. The disease can disappear without a trace.
Youthful kyphosis is treated comprehensively: massage, special exercises to strengthen the muscle corset, drug improvement of trophic bone-joint system. Often it is necessary to apply surgical methods of therapy: various types of instrumental fixation of the spine.
Lumbar Deformity
Lordosis - curvature of the spinal column with the formation of a bulge in front. Therapy is based on the fight against the disease that caused the curvature. They use traction, special laying of the patient, physiotherapeutic procedures, physiotherapy exercises and general strengthening massage courses.
Causes of lumbar lordosis:
- deformation to compensate for rickets and tuberculosis kyphosis;
- dislocation of the hips that arose during childbirth;
- hip contractures.
Scoliosis
Scoliotic deformity of the spine can affect any level of the spine and affect several sections, causing S-shaped curvature. The disease is more prone to prepubertal girls.
- Congenital scoliosis is associated with the presence of fusion of several vertebrae, the presence of additional vertebrae, an abnormality of the structural components of the vertebra. It occurs in babies under the age of 1 year. It progresses slowly, the bend lines are not pronounced.
- Dysplastic scoliosis is formed during the pathological development of the lumbosacral region. It is found at the age of 9-11 years and progresses rapidly. The curvature line is observed in the lumbar region.
- Neurogenic scoliosis develops due to poliomyelitis, syringomyelia, myopathy. The development mechanism is associated with damage to the motor roots of the spinal cord. Functional muscle failure develops. In parallel, dystrophic changes in the spine occur.
- Rickets scoliosis. Due to impaired calcium metabolism, bone tissue becomes soft. Under static loads, there is an increase in physiological bends. With an incorrect position of the body in space, scoliosis quickly forms.
- Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common spinal deformity. It is a multifactorial disease: impaired spinal growth rate, neuromuscular insufficiency, an active period of growth in children and an increase in physiological stresses on the skeleton. There is a violation of endochondral bone formation in the vertebrae with the subsequent development of osteoporosis and spinal disorders.
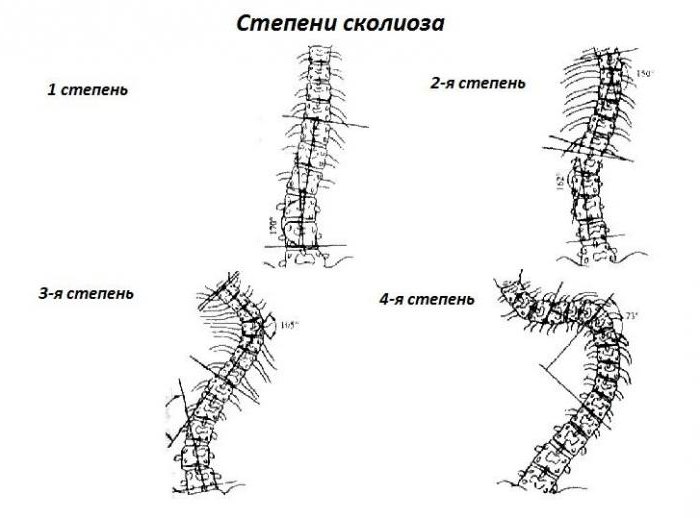
In 1965, V. D. Chaklin radiologically identified 4 degrees of spinal deformity in scoliosis:
- 1st degree - 5-10 degrees;
- 2nd degree - 11-30;
- 3rd degree - 31-60;
- 4th degree - more than 61 degrees.
Clinical manifestations of scoliosis:
- At the 1st degree, in a standing position, weakness of the muscular corset of the back and abdominal wall, different levels of the shoulders, the angles of the shoulder blades are located at different levels, asymmetry of the waist triangles. In the thoracic region, curvature is noticeable, in the lumbar region, on the opposite side, a muscle seal, which is also visible when the body is tilted forward. The x-ray shows no signs of vertebral rotation. The pelvis is located in a horizontal plane. In the supine position, weakness of the abdominal muscles is noted.
- At the 2nd degree, the S-shaped curvature of the spine is visually determined. There are rotations of the thoracic vertebrae, chest deformation occurs. The tilt test shows the protrusion of the ribs on one side or the muscles of the lower back. Progression goes while the child is growing.
- With the 3rd degree, pronounced deformation of the skeleton is determined. The rib hump and pelvic distortion are clearly visible . The line of the shoulders coincides with the line of the pelvis. The venous plexus of the spine is compressed. There may be disorders of the respiratory system.
- At the 4th degree, a severe degree of deformation of the entire body is observed. Growth stops, the relationship of internal organs is disturbed. Squeezing of the spinal cord leads to the development of paresis. On the roentgenogram, wedge-shaped vertebrae are detected.
Scoliosis is a serious disease that can lead to permanent disability (disability).
Scoliosis treatment
Spinal deformities in children should be detected in the initial stages. In such cases, you only need posture correction, physical exercises, swimming, organizing the right work space, maintaining an adequate mode of work and rest, proper nutrition.
Non-surgical treatment is aimed at fixing the spine in the correct position by wearing corrective corsets, training back muscles and abdominals. The child’s room should have a special bed with a hard mattress and orthopedic pillow.
The second degree is treated conservatively, with the progression of the process, children are sent to specialized sanatoriums. A planned course of non-surgical treatment in the departments of orthopedics is carried out. Use the traction method using lateral traction. Such treatment lasts 2-4 months. Traction is often a preoperative preparation at the 3rd and 4th stages. The achieved level of correction is recorded promptly with the help of special tools.
Indications for surgical treatment
- Aesthetic defect that bothers an adult or parents of a small patient.
- The angle of curvature is more than 40 degrees, but with incomplete growth.
- Any deformation is greater than 50 degrees.
- Persistent neurological complications and pain.
- Deformations accompanied by a violation of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Types of Surgical Treatment
There are 3 ways: operations with front access, with rear and combined. The essence of operations is the introduction of metal structures into the spine, which can be static and mobile. Advantages of a dynamic implant: it can be adjusted, ensuring the correct growth of the child, and allows you to play sports. The design is not visible and can be used in the treatment of severe spinal deformities in adults. It allows you to fix the curvature and stop its progress.
Spinal curvature prophylaxis
- Early detection of congenital curvature of the spinal column (orthopedic examination in the maternity hospital is carried out at 1, 3, 6 months and a year) and their correction.
- Identification of acquired deformities in preschool and school age at medical examinations and the application of appropriate measures to correct them.
- Control over your posture. From childhood, you need to teach children to keep their back straight. School institutions should have desks with adjustable table and chair heights. During operation, it is necessary to take short breaks while walking in order to avoid static load on the spine.
- Timely detection of rickets, polio, tuberculosis and appropriate treatment.
- Preventive courses of general massage for passive strengthening of the muscular corset.
- Exercise in order to strengthen the muscles of the back and abs.
- Swimming.
- In the absence of limbs, it is necessary to solve the issue of prosthetics.
- Wearing orthopedic shoes with different lengths of legs.
- When lifting weights, it is necessary to evenly distribute the load on both halves of the body.
- Eat properly, food should be balanced in terms of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Avoid overeating and gaining excess weight, which is an additional factor in the development of spinal deformities.
- Avoid prolonged position in one position, arrange physical exercises.
- Organize the correct sleep mode. The bed should be hard, and it is better to purchase a pillow orthopedic in a special salon.
- In case of visual impairment, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist (with low vision, a person can take a forced position, stretch his neck and aggravate cervical lordosis).
- Fight depression and apathy.
- Observe precautions to prevent injuries.
- In time to treat hernias, osteochondrosis, spinal tumors.
Timely treatment can completely relieve spinal deformity.