Adenoiditis can be detected by characteristic symptoms, without even having to examine it with a mirror. With the disease, nasal breathing is disturbed, hearing loss is observed, the voice changes, it becomes nasal. The more the pharyngeal tonsil increases , the more these symptoms manifest themselves. Chronic adenoiditis can change the severity, there are only three of them - I, II, III. The disease develops in young children. Adenoiditis is masked for colds, SARS, which is why it can not be immediately detected. So the disease flows into a chronic form, and this leads to serious consequences.
Chronic adenoiditis
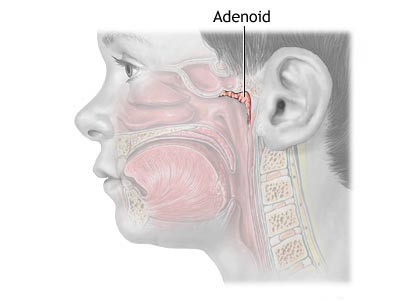
The pharyngeal tonsil in childhood plays a huge role. It produces protective antibodies and is a living barrier to infections that enter the body. A child, visiting public institutions, is always exposed to the risks of infection with bacteria, viruses. With intensive work, the tonsil grows in size, grows and the formation of adenoids occurs. According to the famous pediatrician Komarovsky, it is necessary to begin treatment at the first stages, so as not to bring the matter to surgical intervention. Educated adenoids are often inflamed due to infections, and adenoiditis develops in children. Symptoms and treatment Komarovsky, like any other pediatric doctor, knows perfectly. Depending on the stage, the correct method of getting rid of the problem is prescribed.
Chronic adenoiditis leads to a constant runny nose, since the inflamed tonsil in the pharynx closes the lumen, breathing is disturbed. Chronic adenoiditis in a child (2 years) can have an initial stage, most often the disease affects children from three to ten years. The child begins to breathe more often with his mouth, in his sleep - snoring. Accumulated mucus often provokes a cough with adenoiditis.
Medical statistics say that 20% of young children suffer from chronic forms of adenoiditis. In adolescents, the nasopharyngeal tonsil begins to decrease and by the age of 20 it completely atrophies. Its maximum size is reached at the age of 4 to 7 years. But it is not necessary to say that by the age of 14-15 the sore will resolve itself. Adenoiditis requires immediate treatment, as the consequences can be very serious.
Factors contributing to the disease
Chronic adenoiditis is formed in the presence of frequent bacterial and viral infections. Other reasons:
- weakened system of the child;
- allergic diseases;
- persistent colds;
- hypothermia;
- artificial feeding;
- lack of vitamin D;
- chronic infections;
- excess in the diet of carbohydrates;
- poor environmental conditions;
- too humid or too dry air in the room;
- hormonal disorders.
Exacerbation of chronic adenoiditis occurs in the presence of acute viral infection, with the active reproduction of pathogenic bacteria. Other causes of exacerbation:
- Inflammatory ENT diseases (ARVI, whooping cough, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, measles).
- Hereditary factor.
- Overfeeding with carbohydrate food, sweets.
- Insufficient immunity, a tendency to allergic reactions.
Violation of the temperature regime in the room (too warm, dry air, a lot of dust, harmful substances - household chemicals).
Adenoiditis in children, symptoms and treatment (Komarovsky)
According to Dr. Komarovsky, the transition of acute adenoiditis to a chronic form can be determined by the following symptoms:
- the mouth is constantly ajar;
- appetite is reduced;
- having trouble sleeping;
- the nose is blocked, as a result - sniffling, snoring;
- rhinitis occurs with mucus and pus;
- low-grade fever (temperature from 37 to 37.9)
- there is a lag in mental and physical development;
- headache;
- bouts of night cough due to accumulated mucus in the throat;
- fatigue;
- hearing loss.
Chronic adenoiditis symptoms are similar. In this case, the child’s speech is disturbed. The kid hardly pronounces nasal consonants, tries to speak muffledly, abruptly, “in the nose”. Even in appearance, a child can have adenoiditis in a chronic form. A so-called "adenoid face" is formed - the lower jaw sags, salivation increases, swelling appears and the bite is broken. Oxygen starvation is a consequence of difficulty in nasal breathing. Children with such a pathology often have a narrowed and protruded chest.
Often chronic adenoiditis is accompanied by pharyngitis, bronchial asthma, tonsillitis. This is due to the constantly open mouth, through which infections quickly penetrate the body, settle on the larynx, trachea. Inflammatory processes can spread in the nasal cavity, as a result - constant mucus discharge, and this leads to skin irritation on the lips, redness, painful microcracks appear.
Diagnostics
The treatment of adenoiditis is performed by an otolaryngologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor makes an examination and listens to complaints. A good specialist can suspect adenoiditis even if it is detected:
- redness, swelling of the pharyngeal tonsil;
- purulent, mucous discharge.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Back rhinoscopy. Using a mirror, the doctor examines the posterior sections in the nasal cavity. This allows you to identify the extent to which adenoids have grown, hyperemia (redness), the presence of pus, swelling is established.
- X-ray of the nasopharynx. Differential diagnosis of adenoiditis and sinusitis. Severity rating.
- Endoscopy of the nasopharynx. An elastic tube with a video camera is used, which allows you to identify the exact size of the adenoids, their condition, as well as the mucous membrane.
- A swab from the nasopharynx. Allows you to determine the sensitivity to certain medicines, and also identifies pathogens.
- Methods of otoacoustic emission and audiometry. These studies are conducted if the patient has a hearing loss.
The doctor must differentiate chronic adenoiditis from the following diseases: sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, juvenile angiofibroma (in adolescents).
Treatment methods
Adenoiditis is treated both with medical methods and surgical. Komarovsky and other doctors recommend conducting treatment of adenoids in children without surgery at stage I or II. Drugs should be prescribed by the attending physician. Most often, complex therapy is used - local antibacterial agents plus antihistamines.
Nasal lavage with special solutions is also prescribed. This procedure is useful not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of the disease. Washing the nasopharynx removes the mucus, and with it all the microbes. At the same time, nasal congestion decreases, the degree of inflammation decreases. The procedure should be repeated 3-4 times, during an exacerbation of the disease - up to 6 times a day. For washing, you can use: a syringe or a children's aspirator; Esmarch's mug; a syringe without a needle; special pharmacy devices. In the form of a solution are suitable: saline solutions, infusions of herbs, medicines, natural mineral water. During the washing procedure, safety precautions should be followed and liquid should not be allowed to enter the auditory tube, this can contribute to inflammation of the middle ear and hearing impairment.
Physiotherapeutic treatments
Komarovsky recommends including physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of adenoids in children without surgery. The otolaryngologist must choose effective methods, they will depend on the severity of the disease, the size of the adenoids, and the degree of inflammation. The most common method is laser therapy. The procedure uses helium - a neon laser. With its help, adenoids warm up, while all microbes die, edema and inflammation decrease. For the effectiveness of the procedure, the following conditions should be observed:
- The LED tube must be connected directly to the adenoids; irradiation through the bridge of the nose will not bring the desired result.
- Before the irradiation procedure, it is necessary to rinse with saline, eliminate all mucus and pus from the nasal passages.
Ozone therapy is also considered an effective method; here, ozone gas is used. With it, you can stop the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, local immunity is restored, healing of the mucosa is accelerated. Ozone is easily soluble in water, so it can be used when washing the nasopharynx.
UFO method. Ultraviolet rays have bactericidal properties. After 3-8 hours of use, a positive effect is observed.
Ultra high frequency therapy. Often used during an exacerbation of the disease. Pulse currents of ultra-high frequency can eliminate the inflammatory process, reduce pain, increase local immunity.
Magnetotherapy. Accelerates cell recovery, increases the protective functions of the body.
Electrophoresis In this method, various drugs (antihistamines, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs) are injected through the mucous membranes and skin using an electric current.
EHF therapy. Electromagnetic waves having a millimeter range are used. The procedure relieves edema, improves immunity.
All these procedures can bring success in treatment, mainly in the early stages of the disease. If it is running, you may need an operation to remove adenoids.
Surgical intervention
Thinking about the question of how to cure chronic adenoiditis in a child, be sure to consult a doctor. It often happens that surgical intervention is required. An absolute indication for this is obstructive sleep apnea. In addition, surgery is required in cases where other methods only temporarily relieve symptoms of chronic adenoiditis.
Tonsil removal is performed under stationary conditions, the operation is called adenotomy. The doctor will advise if the child should remove adenoids. If the operation is inevitable, he will prescribe one of the types of surgical intervention, it can be:
- The classic operation.
- Endoscopic surgery.
- Laser adenotomy
After the operation, the patient is prohibited from intense physical activity, swimming, eating hot, sour foods and drinks.
The treatment of adenoids with folk remedies is the most effective
With the course of the disease not in severe form, along with drug treatment, you can use traditional medicine recipes as an adjunctive therapy. If adenoids are found in children, treatment at home can be carried out in the following ways:
- Saline flushing. Dilute a teaspoon of salt in a liter of water, repeat three times a day.
- Aloe juice. After washing with salt water, drip 3-5 drops of fresh aloe juice into the nose. The course continues - 60 days.
- Sea buckthorn oil. There are three drops in each nostril. The course is three weeks.
- For washing the nose - propolis. Take a pharmacy tincture, dilute 20 drops in a glass of water (warm), add a quarter teaspoon of soda. Do washing three times a day.
- Honey with beets. Proportions ½ (honey + beetroot juice). Three drops are instilled three times a day. The course is three weeks.
- Herbal collection for rinsing: chamomile - 3 tsp, linden - 2 tbsp. - pour a glass of boiling water, insist 20 minutes, drain. Rinse the nasopharynx three times a day for a week.
- Infusion: take 100 g of mint, wheatgrass, sage, coltsfoot, chamomile. Three tablespoons of the collection pour 750 ml of boiling water. Insist 20 minutes, strain. Drink a glass three times a day after meals.
- Inhalation with adenoiditis is done with essential oils. Lemon oil or eucalyptus is suitable. Three drops of oil are dripped into the inhalation cup. You need to breathe for at least 10 minutes. For babies, the dose and time are halved.
Breathing exercises
So, if you started treatment of adenoids with folk remedies, the most effective recipes do not guarantee complete elimination of the problem. Use breathing exercises at the same time. It helps to avoid possible exacerbations and the transition to the chronic stage. If adenoiditis is chronic, respiratory gymnastics preserves nasal breathing and prevents the development of hypertrophy of adenoids. Exercise during periods of remission. The main goal is to teach the baby to breathe through the nose correctly, so that the body is saturated with oxygen, lymph outflow occurs. As a result, adenoids decrease. In the chronic form of adenoiditis, the following exercises are useful:
- Breathe one nostril. Inhale the right (hold the left at this time), exhale the left (hold the right at this time).
- Gurgling. Submerge the rubber tube in the bottle, the other end into the mouth. The baby should inhale through the nose, and exhale into the tube. Gurgle like that for five minutes. Inhale, exhale.
- Hedgehog. Let the kid imagine that he is a hedgehog looking for apples in the grass. Take a deep breath and turn your head to the right, then to the left.
- The crane. Inhale through the nose, arms reach up. Exhale, hands fall.
- Ball. Smooth breath, inflate your stomach. Exhale - blow out your stomach.
Doing breathing exercises is better in the morning. Before classes, rinse your nose well, drip drops.
Prevention
If adenoids are found in children, treatment at home will not give an instant result. For consultation, be sure to contact the otolaryngologist. A knowledgeable specialist will tell you the correct methods. Well, in order to prevent adenoiditis, parents should follow the recommendations:
- Call your doctor right away as soon as you notice snoring in a dream, congestion, open mouth, and hearing loss.
- Colds must be cured to the end.
- Increase the body's defenses, immunity by hardening, physical education, vitamins, proper nutrition.
- Limit the child's contact with patients with acute respiratory infections.
- Hygienic procedures should be carried out regularly - brushing your teeth, flushing the nose with saline solutions, gargling after eating.
Adenoiditis can lead to serious consequences, affect development, so parents at the first suspicion are required to show their child to a doctor.