Tonsil inflammation, symptoms whose treatment is known to almost every person, remains the most common infectious disease. About 15% of the world's population suffers from a chronic form of tonsillitis. Angina with inflammation of the tonsils is quite difficult: the body temperature rises, pain is pronounced, sometimes the processes of breathing and swallowing are even disturbed. Especially often children suffer from the activity of lymphoid tissue. Few people did not worry about the removal and treatment of adenoids, tube tonsils, tonsils of the palate. Let's try to understand the reason and determine the correct approach to the treatment of inflammation.
Building and purpose
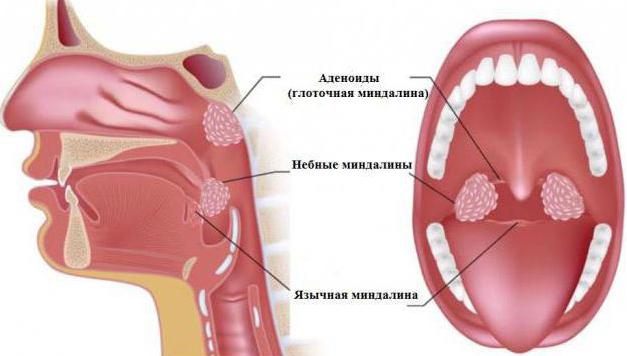
The pharynx is the connection between the oral cavity, nasal passages, ears, larynx and esophagus. In total, six tonsils are located along its length: two palatine and trumpet, pharyngeal and reed. They consist of lymphatic tissue, which constantly produces lymphocytes and other cells to protect the immune system. Together, all the tonsils make up the pharyngeal “ring”. It does not pass harmful bacteria with the air that we breathe into the body.
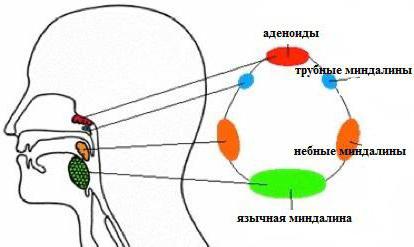
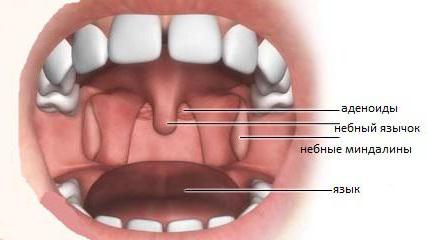
Palatine tonsils are located on the right and left pharynx. You can see them yourself in the mirror, wide open mouth. Most often it is they who take the brunt, which leads to a painful sore throat. Tubal tonsils are located deeper: in the area of the swallowing hole adjacent to the ear canals. They got this name because of the Eustachian tubes that are nearby. The junction of the oral cavity and nasopharynx is protected by the pharyngeal tonsil. And the closing link of the pharyngeal ring is the lingual tonsil, located at the base of the tongue on the back side. The glands of a healthy person cope with any infection without blocking its entry into the body.
Tonsil inflammation in adults and children primarily indicates a decrease in immunity. Lymphocytes and other cells could not delay the infection, and the disease began to develop. The site of infection by bacteria becomes inflamed. And tonsils react in the first place.
Tonsil inflammation in the throat: causes
Sore glands always cause infection. It enters the oral cavity and nose in various ways. Most often, the disease develops according to the following scenarios:
- The impact of pathogenic microorganisms: streptococci, pneumococci and other similar bacteria, followed by infection of the whole organism.
- Hypothermia combined with a weak immunity with the further development of tonsillitis.
- Infection from a patient with an infection that provokes inflammation of the tonsils. Symptoms and treatment usually coincide with the picture occurring at the source.
- The development of the disease due to tooth decay, gum disease, a constant cold.
By the nature of the pathogen, tonsillitis is distinguished by viral, bacterial, fungal or herpetic origin.
Catarrhal sore throat - the easiest form of inflammation of the tonsils
The defeat of the surface layer of the glands indicates the occurrence of a catarrhal sore throat, the causative agent of which is most often streptococcus group A. This is the initial stage of the inflammatory process, which can go into the form of lacunar, follicular or phlegmonous tonsillitis. Adults tolerate the disease quite easily, which can not be said about children. It is worth paying attention to the fact that catarrhal sore throat with serous plaque is the main sign of scarlet fever.
The main symptoms of damage to the outer shell of the tonsils include:
- sharp sore throat that interferes with normal swallowing;
- subfebrile temperature, sometimes fever up to 40 degrees (especially in children under 3 years old);
- intoxication of the body;
- redness of the tonsils, their swelling, lack of plaque (with diphtheria and scarlet fever, serous plaque);
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw;
- general weakness, soreness in muscles and joints;
- fever in the throat.
Inflammation of the tonsils in a child with catarrhal sore throat is accompanied by severe sore throat and leads to rapid loss of fluid. The general condition is weak and requires a sparing regimen of the day. It also happens that children suffer a sore throat easily. Adults do not experience severe malaise and quickly restore health.
Treatment of catarrhal sore throat
Even mild inflammation of the tonsils in a child is often accompanied by a serious condition: high fever, weakness, sharp pains in the throat. If you find the first symptoms, you should definitely call a doctor, because angina is a concomitant sign of many infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever). After examining a doctor, the best tactic will be strict adherence to all prescriptions in order to eliminate tonsil inflammation, symptoms. Treatment in a child is usually based on penicillin antibiotics, bed rest and vitamin therapy. Additionally, you can use rinses from decoctions of chamomile, celandine, and other medicinal herbs. It is necessary to ensure that the baby consumes a sufficient amount of warm liquid.
Treatment in adults is carried out depending on the general state of health and the clinical picture. But for faster and more effective recovery, antibiotics are prescribed. Various sprays, antibacterial plates for resorption, rinsing relieve inflammation. To prevent the development of complications, it is recommended to observe bed rest until the body is completely restored.
Severe palatine tonsil lesions
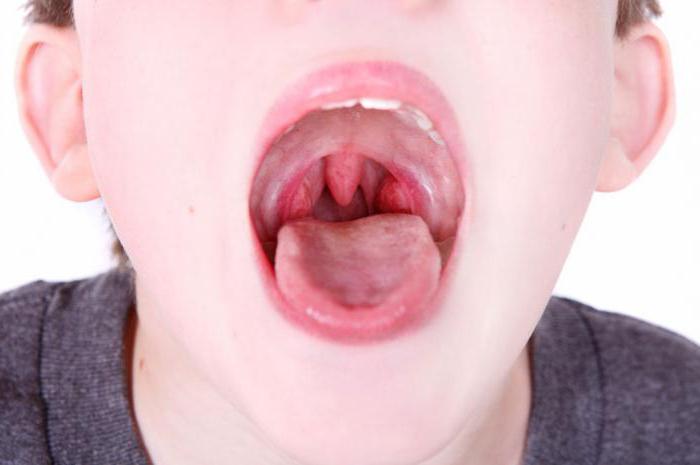
With poor treatment of superficial inflammation, the disease progresses to deeper glands: gaps. A white coating or even separate purulent follicles is formed. Angina passes into a severe form, requiring high-quality treatment. There are lacunar and follicular types of the disease. They differ in characteristic signs, and sometimes occur on different sides of the pharynx at the same time.
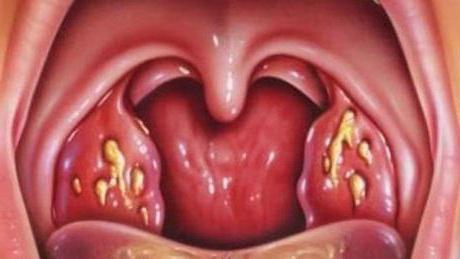
Purulent inflammation of the tonsils causes rapid reproduction and vital activity of cocci. The disease is accompanied by:
- dry mouth and constant thirst;
- cough, sore throat;
- severe pain that swallows in the ear;
- the formation of follicles (yellow-dirty "grains") with pus inside;
- general weakness, high fever;
- constipation in adults, vomiting, or diarrhea in children.
The condition is dangerous with complications for the heart and kidneys. That is why it is extremely important to be treated correctly and not to neglect the regimen. Lacunar tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, symptoms whose treatment is very similar to the follicular type of the disease. A distinctive feature is the formation of white plaque and a sharp sore throat that occurs suddenly. Already in the afternoon, a person may not feel unpleasant sensations, and already in the evening there will be all the signs of angina. There are frequent cases when a follicular type developed on one of the palatine tonsils and a lacunar type on the other.
Methods of treatment of follicular and lacunar tonsillitis
For both an adult and a child, purulent inflammation of the tonsils is very dangerous. Treatment should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician. Two methods are provided: medication and surgical. Of course, the main therapy can be reinforced with folk remedies to reduce inflammation of the tonsils, symptoms. What antibiotic treatment is carried out? Usually, the use of a wide range of medicines is envisaged: penicillin rows, Erythromycin, Sumamed. In case of viral damage, antiviral drugs are used. Prescriptions should be carried out only by a doctor, taking into account the nature of the course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. In addition to antibiotics, prescribe:
- follicular washing with antiseptic solutions;
- suction of pus by vacuum;
- local injection;
- treatment of tonsils with an oil solution that promotes healing;
- physiotherapy;
- vitamins and immunostimulants.
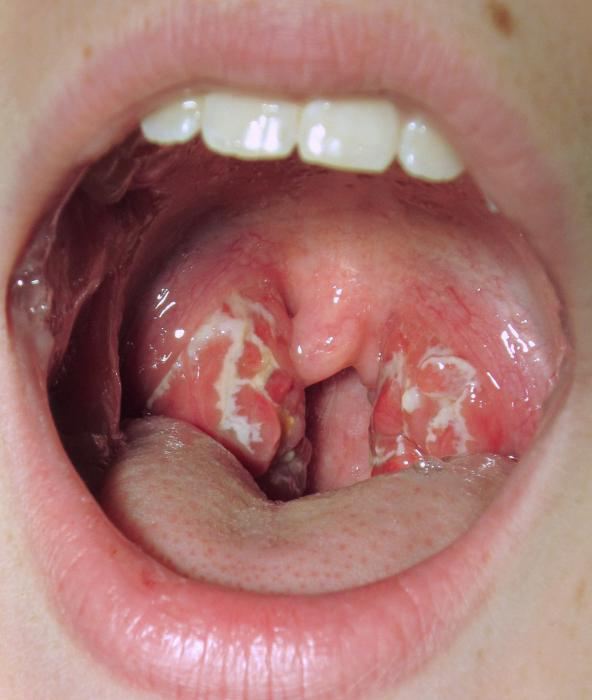
It is necessary to pay attention to childhood inflammation of the tonsils. Symptoms, treatment Komarovsky distinguishes from the adult course of the disease. According to a famous pediatrician, the use of antibiotics is a prerequisite, otherwise tonsillitis cannot be cured. In addition, most rheumatic diseases and heart diseases develop precisely due to the activity of cocci with angina. Penicillin rows are considered the safest and are recommended even for newborn children. In addition, it is necessary to provide the child with a plentiful warm drink and food in the form of soft mashed potatoes and cereals.
Phlegmonous inflammation of the tonsils: symptoms, treatment, photo
Phlegmonous tonsillitis - or purulent acute inflammation of the fiber near the tonsils - a frequent complication of tonsillitis. It usually occurs 1–2 days after inflammation of the tonsils. Phlegmonous tonsillitis is one-sided. It rarely develops on both palatine tonsils. It is characterized by acute pain when swallowing, fever, weakness, and excessive salivation. The affected tonsil increases in size and moves to the center of the larynx with pulling down.
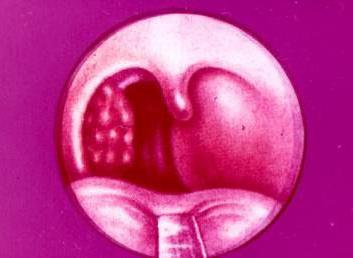
Delayed treatment can provoke the occurrence of an abscess, which is confirmation of the diagnosis - "phlegmonous inflammation of the tonsils." Symptoms, antibiotic treatment is similar to the previous case. The main rule: you need to start taking medications as quickly as possible. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics (penicillin rows, "Erythromycin" "Sumamed"), as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulants. In the early days of treatment, the patient should observe bed rest. With the formation of an abscess, it is opened surgically. Then washed, if necessary, remove the palatine tonsils in order to avoid complicated conditions.
Pharyngeal tonsil inflammation
The nasopharyngeal tonsil, popularly referred to as adenoids, is the first line of defense for nasal breathing. At the slightest sign of disease, they increase in size. If diseases occur frequently, with an interval of less than one week, the tonsil does not have time to recover and chronic inflammation develops. Most often, adenoids increase in childhood, because they play a major role in protecting the body from infections. After 13-15 years, they decrease in size and are practically not inflamed anymore.
Provokes the proliferation of lymphatic tissue frequent runny nose. Inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil should be suspected if there are signs:
- lingering runny nose, which is difficult to treat;
- difficulty in nasal breathing and lack of a runny nose;
- frequent breathing through the mouth, especially at night;
- colds, the interval between which is only 1-2 weeks.
They provoke inflammation of adenoids and infectious diseases. For example, scarlet fever, measles, whooping cough, flu. Often, parents are not even aware of problems with the pharyngeal tonsil, which indicates a poor awareness of the signs of their growth and proliferation. The chronic process can lead to complications from the heart, kidneys, musculoskeletal system. Respiratory disturbance, numerous tissue growths sometimes even lead to defects in the upper jaw.
Adenoiditis Treatment
Success in the fight against sore throat tonsils depends on many factors: the approach to treatment, the qualifications and experience of the doctor, as well as the lack of rush. It is also worth considering that with any cold, adenoids increase. And this does not always indicate the development of adenoiditis. Often after recovery, they return to normal. Another thing is when the infection is not healed in a hurry, and the weakened child picks it up again. The tonsil does not have time to recover and becomes inflamed again, which provokes proliferation.
There are two approaches to the treatment of adenoids: conservative and surgical. First of all, it is recommended to try all possible methods of drug exposure:
- rinsing the nose with saline, decoctions of herbs and special preparations;
- the use of anti-inflammatory drops;
- general immunotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
If after a long and stubborn struggle, adenoids do not decrease in size, but only grow, most likely, you will have to resort to surgical removal. It is a mistake to think that after this the child will cease to be ill at all. Yes, this is a huge focus of infection. But he poses a threat only with significant growth and serious violations of nasal breathing. If there is no pharyngeal tonsil, the infection will spread throughout the body faster and find a loophole for its comfortable existence. Adenoiditis will be replaced by tonsillitis or otitis.
It should be remembered that the removal of adenoids is not a solution to the problem of weakened immunity and frequent colds. This is an extreme measure, which is justified to go only with a significant increase in the tonsils and the absence of the effect of conservative treatment. The removal is performed by an ENT surgeon using a special loop under local anesthesia. Endoscopy is considered a more modern method, which requires general anesthesia and allows you to completely get rid of the vegetative growths of adenoids and avoid relapses.
Tonsil inflammation: symptoms, treatment of lesions of the lingual lymphoid tissue
The lingual tonsil is located on the back of the tongue on the back side. Her tissue is inflamed extremely rarely. If the lesions still begin, then usually against a background of catarrhal, follicular, or phlegmonous tonsillitis. Acute inflammation of the tonsils of the palate or pharynx indicates an extensive localization of the infection, which also joins the tongue. In this case, the clinical picture is characterized by pain in the movement of the tongue and its swelling, significant difficulties in chewing and swallowing, and speech impairment. The remaining symptoms coincide with signs describing inflammation of the tonsils. The temperature is low-grade, can rise to 39–40 degrees.
The treatment approach is based on the use of antibiotics, bed rest and restorative drugs. The lack of effect from medications is explained by individual resistance to the action of drugs or the development of a hyoid abscess. In order to avoid complications, inflammation of the lingual tonsil should be treated by a qualified specialist - ENT.
Tube Tonsil Defeat
Tube lymphoid tissue is located near the Eustachian tube on both sides of the jaw. Inflammation of these tonsils is often attributed to ear diseases, because pain occurs in this localization. From otitis media, lesions of the tubular formations are distinguished by the following signs:
- the primary source of pain is the throat, after which discomfort occurs in one ear or two at once;
- mucous or purulent discharge flows down the back wall of the pharynx;
- the lymph nodes under the jaw are enlarged, and the parotids do not increase at all or slightly respond to infection;
- intoxication of the body is observed.
As with inflammation of other tonsils, the disease is more severe in children than in adults. The condition is accompanied by high fever, often coughing, cramps, vomiting. The approach to alleviating the patient’s condition is based on the same principles that are used to eliminate infectious inflammation of the tonsils. Treatment is based on a course of general antibiotics or antiviral drugs (depending on the pathogen). It is additionally recommended to provide the baby with a warm drink, soft and liquid foods, as well as a good rest. Taking immunostimulants and vitamins will only improve the condition and speed up recovery.
Tonsil inflammation is the most common ENT disease, especially in childhood. This is explained by the function that nature has endowed them. Forming a pharyngeal ring, lymphoid tissue produces antibodies and lymphocytes that are actively fighting any infection that enters the body. A healthy person with strong immunity has practically no problems with tonsils - they do their job well and manage to recover.
But with weakening of the body, which contributes to prolonged hypothermia, stress, poor sleep and nutrition, strong protection is destroyed, and tonsils can not cope with their task. Inflammation develops. Only a correct understanding of the essence of the problem will help to avoid problems with swelling and proliferation of lymphoid formations.Remember that tonsils are not to blame, but a weakened state of the body. The first step to treating an adult or child should be a trip to an immunologist and increased attention to health.