The spinal column of an adult is a support for the whole body and can withstand heavy loads. If you lift the weight on outstretched arms, then the load increases to 400 kilograms. The largest falls on the lumbar, because this is one of the most mobile parts of the trunk, and the center of equilibrium is localized here. In this regard, all the factors described above provoke the development of a hernia of the lumbar intervertebral disc , the symptoms of which are simply impossible to miss.
And a hernia arises because, due to serious loads, the disks between the vertebrae, which act as a shock absorber, wear out earlier than in any other departments.
Lumbar discs differ from others in their unique structure. In their center there is a jelly-shaped egg held by a fibrous ring. But hernias are found in other parts of the spine, and there are many reasons for this.
Causes of the appearance of intervertebral hernias
There are many causes of herniated discs. The disease is often a complication after pathologies such as scoliosis, osteochondrosis, lordosis and excessive kyphosis. A hernia can develop as a result of a spinal injury when falling on your back or banging hard.
The disease may occur due to a power failure of the drives. They do not have a single blood vessel, and the condition of the intervertebral cartilaginous discs is completely dependent on the deep muscles of the back. If they are lightly loaded, then the power of the disks decreases, they lose their strength.
Risk factors for the manifestation of a hernia of the intervertebral disc include:
- 30 years old and tall;
- sudden movements affecting the spine: falls, bumps and turns;
- the female sex, because it is he who most often suffers from the disease;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- severe physical exertion;
- long sitting in one position;
- long driving a car;
- smoking;
- impaired posture;
- large body weight;
- hypothermia.
Patients who are at risk should periodically change their location, for example, if he sits at a computer or driving a car for a long time. Be sure to undergo an examination or do gymnastics in order to improve nutrition of the muscles of the back.
Types of hernia of the spine
Herniated discs are classified according to where they are located. Therefore, there may be hernias of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral. As statistics show, most often doctors after examination identify these types of hernias:
- Central, or hernia of Shmol. This species is not acquired, since it does not arise due to the influence of external factors that affect the spine, but is considered a congenital ailment. With this form, there is no protrusion, but there is an indentation at the site of the lesion.
- Medial is a mystery for doctors, since it is not clear for what reasons and goes without treatment. It is accompanied by severe pain, which goes from a strong degree of intensity to a weak one.
- The dorsal view provides a protrusion of the hernia into the region of the spinal canal, which is the reason for the infringement of the roots of the nerves. At the initial stage, pain with this form is localized in the lumbar region, but with time it can also give off to the leg.
- Sequestered hernia of the intervertebral disc, the treatment of which requires an experimental approach, is manifested as a result of a violation of the integrity of the disc, which leads to the exit of the pulpous nucleus into the lumen of the canal. With this form, the quality of life of the patient suffers significantly. This species manifests itself most often in the neck and lower back.
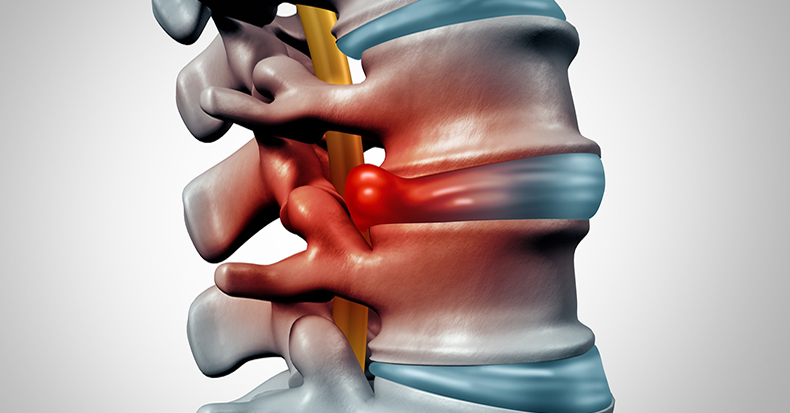
Any of the species requires high-quality professional treatment, therefore, with the first symptoms, it is better to consult a specialist.
How is a hernia formed?
Initially, there is a slight displacement of the intervertebral disc by a couple of millimeters, which is called prolapse. A 4 mm offset is referred to as protrusion. There is a displacement, but the pulpous nucleus does not extend beyond the fibrous ring. At this stage, the main symptom is irritation of the spinal root located in the maximum proximity.
With further progression, the hernia leads to a crack in the fibrous capsule and prolapse of the pulpous nucleus. This condition is called extrusion in medicine. At this stage, a hernia of the intervertebral disc can transmit the spinal root and blood vessel, which ultimately causes radiculopathy - this is a radicular syndrome accompanied by neurological symptoms.
Next comes the stage when the fallen pulpous nucleus penetrates beyond the gap between the vertebrae, is designated as sequestration. It is this condition that ends with the rupture of the fibrous capsule and the complete expiration of the nucleus. At the stage of extrusion and sequestration, the hernia grows to such a size that there is a high probability of compression of the spinal cord with the development of compression myelopathy.
Symptoms of intervertebral hernia
At the initial stage, it is difficult to determine the ailment, because it manifests itself in the form of pain. And it can be just a signal that the body is tired and needs rest. But if you do not take any measures, then subsequently you will not be able to miss the symptoms of a herniated disc. The following symptoms can tell about the disease:
- muscle atrophy in the affected area;
- muscle pain in the back;
- headache;
- migraine;
- problems with intestinal microflora, which may result in a disorder or constipation;
- difficulty urinating
- in the place of localization of the hernia puffiness is manifested;
- hypoxia appears in the spinal cord;
- difficulty walking; weak legs;
- drawing pain in the place where the hernia formed;
- numbness of the fingers, tingling sensation in the limbs;
- pain when coughing, turning the body and head;
- acute pain when moving, which is not able to endure.
If at least one of the symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar intervertebral disc appears, treatment must be started urgently to prevent complications that can only be removed surgically.
Complications of an intervertebral hernia
There are several serious forms of intervertebral hernia complications. They appear in patients who are self-medicating and do not want to seek help from a doctor.
Radicular syndrome manifests itself at the moment when the hernia acts on the spinal nerve. This complication can develop in stages: initially a symptom of spine irritation appears, patients feel lumbago or feel like they were struck by an electric shock. In the area of radicular innervation, paresthesia is observed. Loss of root functions leads to the development of muscle weakness, lowering blood pressure and sensitivity in the affected area. After some time, flaccid paresis develops with muscle atrophy and trophic disorders.
Discogenic myalopathy is another complication that forms at the moment when a hernial formation provokes a narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of the spinal substance occurs. Initially, motor function suffers, peripheral paresis develops in the affected area, later a violation of sensitivity and sensitive ataxia are added.
Another complication is vertebral artery syndrome, which occurs if a hernia in the neck compresses a nearby vertebral artery. The syndrome manifests itself in the form of dizziness, vestibular ataxia, tinnitus, fainting. It may even cause circulatory disorders in the brain.
In order to prevent complications, it is urgent to seek qualified help and undergo treatment for a herniated disc of the lumbar spine, the symptoms of which cannot be overlooked.
Diagnostic methods
To establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the form of the disease, the doctor recommends a comprehensive examination, because a hernia between the vertebrae can easily be confused with ankylosing spondylitis and other ailments. To make a diagnosis and identify in which particular department a hernia is present, the following methods are used:
- MRI
- CT
- Ultrasound of the spine;
- X-ray of the spine;
- laboratory research.
All these data can be accurately indicated - this is a hernia of the intervertebral disc l5 s1 or any other department. A hernia L5 S1 is called a formation in the lumbosacral region. The letter L stands for lumbar, or “lumbar,” and S stands for sacrum, or “sacral.” As a result, it turns out that a hernia formed between the 5th vertebra in the lower back and the first in the sacrum.
Conservative treatment
It is very easy to treat an ailment identified at the initial stage. The sooner the patient begins to take drugs, the higher the chance of a complete cure and a return to normal life. Conservative methods include manual massage, physiotherapy, spinal column traction and acupuncture. Additionally, the doctor prescribes a complex of medicines to relieve inflammation and pain:
- as anesthetics, you can stop at "Ketonov", "Baralgin", "Nise";
- To remove the inflammatory process, NSAIDs are selected - Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide or Ketoprofen;
- muscle relaxants - "Midokalm";
- narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics;
- sedatives;
- hormone "Dexamethasone";
- novocaine blockade.
In the most difficult cases, the doctor may recommend surgery. In this case, a hernia of the intervertebral disc is removed and muscle sensitivity is restored.
Surgical intervention
When conservative treatment of a hernia of the intervertebral disc of the lumbar and any other does not give the desired results, and the patient can no longer tolerate the symptoms, the doctor can take drastic measures - surgical intervention. Most often resort to endoscopic discectomy. The hernia is removed using a special tool. The main advantage of this technique is that you do not need to make any large incisions, the patient recovers faster. To remove the protrusion, just make a small puncture. This technique has a number of undeniable advantages:
- no general anesthesia, only local anesthesia;
- there are no violations of the integrity of the bones and muscles of the spine;
- not the next day the patient can return to a full life.
Alternative methods may include nucleoplasty, radiofrequency denervation, and percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Useful exercises
During treatment of a hernia of the intervertebral disc of the lumbar, when pain and inflammation have already been removed, it is useful for the patient to perform daily exercises. Special exercises will help increase the distance between the vertebrae and reduce the size of the hernia. You can perform this complex:
- Lying on your back, lower your arms along the body, raise the body up and hold it for a few seconds, return back. Make 10-15 sets.
- Continuing to lie on your back, arms are also extended along the body, pull the chin to the chest, and pull the socks up. During execution, spinal tension is felt. Repeat the exercise several times.
- Kneeling, hands on the floor. Alternately, you need to stretch your arm forward and the opposite leg to the side.
- Remaining on all fours, bend your back up and down.
Regular exercise will strengthen your back muscles and relieve tension.
Preventative methods
If the patient knows that he belongs to the risk zone, then he needs to do everything possible to prevent the formation of a hernia of the intervertebral disc l5 s1. To exclude the formation of a hernia, doctors recommend:
- Visit the pool regularly.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Go in for sports, even walking can solve the problem.
- When walking, always keep your back straight, do not stoop.
- Sleep on a special orthopedic mattress.
- Watch your weight, because extra pounds is a serious burden on the spine.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Always distribute weight on both hands.
- When working at a computer, recline the back onto the back of the chair, thus reducing stress from the spine.
- If the work involves constant sitting at the table, then every two hours it is better to stretch your back, it is enough to just make turns even in a sitting position.
Effects
If you do not receive timely qualified treatment, then a hernia of the intervertebral disc of the lumbar and any other department can cause serious and irreversible consequences:
- Weakening of the back muscles in the part where the protrusion is present. The patient will not be able to subject himself to physical exertion, even climbing stairs and being on his feet for a long time will cause him severe pain in the back.
- Local deterioration of muscle tone. The patient can not tolerate even minor physical exertion, because the muscles are weakened.
- Muscle atrophy occurs, during which the problem side figure suffers. There is a smoothing of the gluteal fold, the volume of the legs decreases.
- Sensitivity is disturbed at the place of protrusion and along the path of the nerve process.
- Failures in the thermoregulation system, the place where the hernia is localized, dries up or increased sweating is observed.
- Paralysis is a serious consequence that occurs if the patient does not seek timely help or does not follow the doctor’s recommendations. As a result, paralysis leads to disability, it is difficult, and in some cases impossible to return to the usual way of life.
Symptoms of a hernia of the intervertebral disc of the lumbar or any other should make the patient take care of his health and go to the doctor. Timely initiated treatment guarantees a favorable prognosis.