Like rubella, mumps or chickenpox, jaundice is heard by many. She attributed the status of the disease to the people, which is fundamentally wrong. It is also a mistake to put this symptom on the list of "childhood" diseases, harmless and harmless for the most part. In fact, jaundice can turn into a clinic of hepatitis C. It, in turn, without proper treatment becomes a cause of health complications. As a result, the disease associated with the name, giving carelessness and childhood, turns into a deadly killer, whose goal is to decompose the liver.
Hepatitis C - what is it?
In medicine, the concept of "Hepatitis" appeared relatively recently. Only in the early 1970s, scientists were able to discover its A and B varieties. Some time later, in 1989, the causative agent of hepatitis C was also discovered. It is a microscopic viral particle (up to 70 nm) that contains RNA coated with a protein coat. Due to its nature, hepatitis C is a viral disease, the causative agent of which is capable of parasitizing only in the human body.
What is dangerous and how is hepatitis C transmitted? About 400 thousand people die every year in the world due to the virus. The reason for this is life-threatening complications (cancer and cirrhosis), which develop against the background of a chronic variety of the disease. According to statistics, every year 24 people out of 100 thousand become carriers of the virus. The incidence of the disease in the European Region is 1.5%. In total, about 71 million people are infected with the chronic form of hepatitis C in the world.
How is the disease indulged
For a long time, people were massively infected with HCV after a blood transfusion. A similar trend came to naught only when transfused donated blood was checked for the presence of hepatitis C. As for the present, quite often this disease is observed among drug addicts for the same reason. HCV in most cases is transmitted through the bloodstream. This is accompanied by a violation of the principle of one-time use of needles and syringes. Hazards in terms of the spread of hepatitis C are hospitals and other medical facilities that do not comply with the requirements regarding the sterility of the instruments used.
Much less often, the cause is sexual contact with a virus carrier, since in the secretion secreted the number of pathogens is most often minimal. Hepatitis can be transmitted from mother to newborn, but only if she has had an acute form of hepatitis just before delivery. With milk, it is not transmitted, as well as in close contact: with hugs, kisses, in the case of using shared utensils.
Symptoms and signs of hepatitis C
An interesting feature of the disease is that human immunity is able to cope with the virus without outside help. However, this happens infrequently: only 20% of those infected get rid of the virus on their own. Moreover, more than half of those infected do not even suspect this - everything goes asymptomatically. The fight against the virus takes place in the body over a period of two weeks to six months. A person can become a carrier of the virus, while there is no symptomatology, even the level of bilirubin in the blood does not increase. However, in case of successful adaptation of the virus, an acute form of the disease may occur.
The acute hepatitis C clinic is similar to the regular flu clinic. Starting with general malaise, the patient subsequently has a febrile condition. It is accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature and chills, body aches, pain in the joints and muscles. The flu pattern is observed for several days, which is replaced by symptoms characteristic of hepatitis C. First of all, this is a manifestation of jaundice - staining of the eye sclera and skin in a pale yellow color, which is due to an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. The acute stage of hepatitis C is characterized by an increase in liver size. Sharp and aching pains under the right rib are noted. The patient loses his appetite, he is sick after eating. The color of the excretion products changes: urine acquires a dark shade, feces - light.
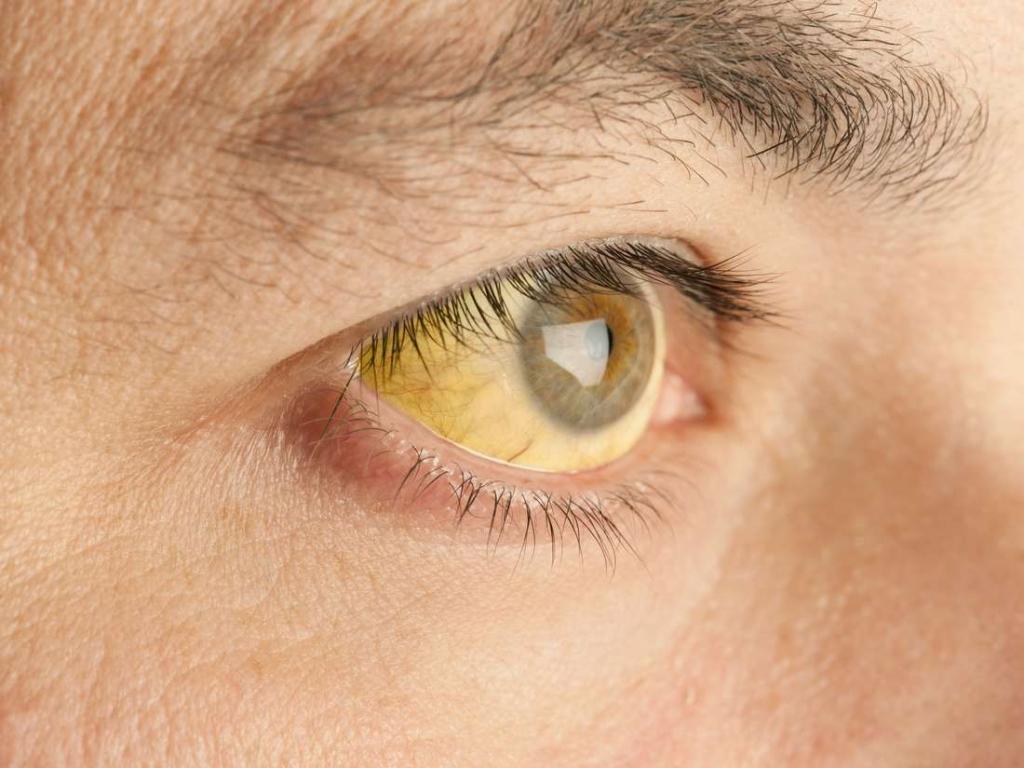
With the appearance of jaundice, negative symptoms are weakened. About 30% of patients recover, while the rest develop a chronic form of the disease. It is the most dangerous for human health and life in general. It is accompanied by a periodically recurring sensation of fatigue, lethargy, headaches, and appetite and digestive disorders. The quality of life is negatively affected by high fatigue and physical weakness. However, the chronic stage of hepatitis C is dangerous, especially because of the high risk of developing life-threatening diseases such as cirrhosis, fibrosis, and liver cancer. During the first 20 years after infection, the risk of developing cirrhosis ranges from 15 to 30%.
Diagnosis of the disease
No wonder hepatitis C is sometimes called a "gentle killer." First, he can skillfully disguise himself as other diseases. And secondly, in many cases, patients do not have any symptoms. For decades, they may not suspect that they are carriers of a dangerous ailment. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C seems to be difficult tasks. Often a person learns that he is sick with hepatitis, by accident. For example, during donation of blood.
Diagnosis of this disease involves laboratory examination methods, including tests and special procedures. First of all, blood donation for AsAT and AlAT is necessary, bilirubin - the so-called biochemical blood test. You also need to donate blood for the presence of anti-HCV bodies. The list of laboratory tests includes PCR for hepatitis C, which detects the presence of virus RNA in the body. As for research, ultrasound (to establish the fact of an increase in internal organs) and a liver biopsy (to assess the degree of its damage) are mandatory for identifying the symptoms of the disease.
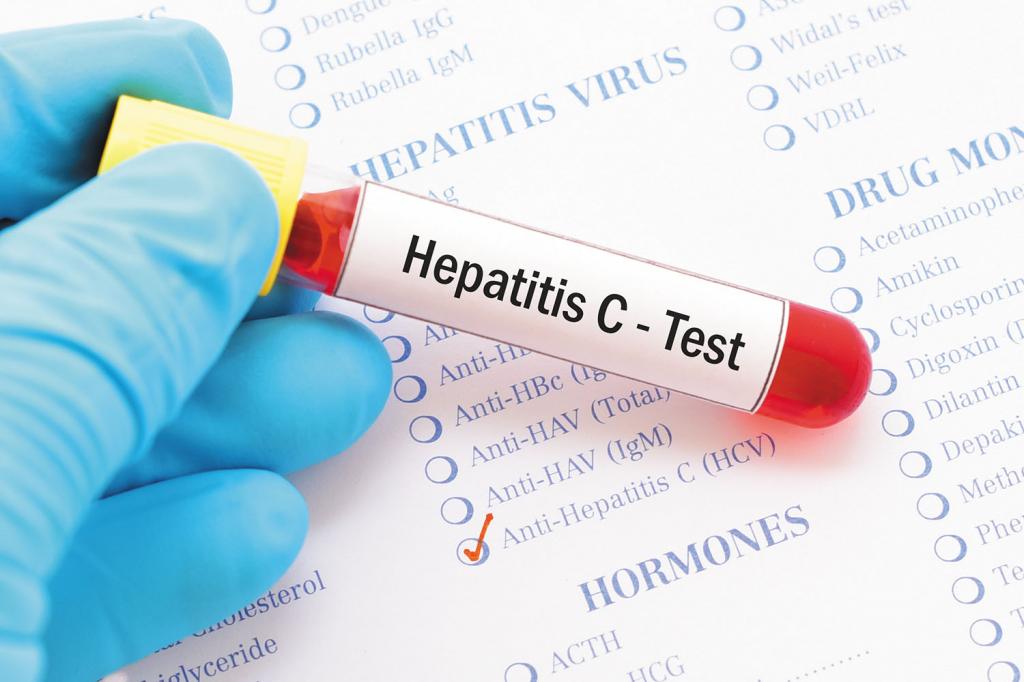
The results presented by the analysis for the presence of anti-HCV bodies in the blood are indicative. If they are present in the body, that is, if the result is positive, then most likely the person is sick with a chronic form of the disease. However, the presence of antibodies may speak of other things. What do antibodies to hepatitis C mean in other cases? On the one hand, they may indicate that a person had previously had hepatitis, but his immune system itself was able to cope with the virus. On the other hand, a positive result may be false for reasons other than hepatitis.
Hepatitis C Treatment
As already mentioned, the disease in 20% of cases does not require treatment due to the strong immune response that destroys the virus. In this case, the patients do not even show the first signs of hepatitis C. Moreover, even if a person is sick with a chronic form of hepatitis, signs of liver damage may not be observed. Therefore, treatment in this case is not vital. If there is a need, then treatment is carried out with antiviral drugs, PPD - with direct-acting drugs. The cure rate, subject to the availability of qualified medical care, is 95%.
The treatment standards themselves are changing rapidly in the modern world. However, the combination with Sofosbuvir and Ledipasvir remains the drug with the best result for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medicines were introduced into use quite recently, but have already managed to prove their effectiveness. They allow you to achieve recovery in a shorter time, on average in 12 weeks. In medical practice, the drug "Ribavirin" is also often still featured, but the World Health Organization recommends gradually abandoning its use. Hepatitis C treatment with Daclatasvir appears to be more modern and effective.

As for surgical intervention, it is necessary only in case of severe damage to the liver. Then the patient needs a transplant. Transplantation will not have the desired effect if the pathogen virus has not been destroyed in the body. Then the hepatitis C clinic in 98% of cases appears again after 3-5 years after the transplant. If the virus is eliminated prior to transplantation, antiviral treatment can be continued even after surgery.
Clinical Treatment Recommendations
The development of key recommendations for the treatment of infectious diseases lies with the World Health Organization. Regarding hepatitis, the recommendations are consistent. The first step is the screening of people who live in the least favorable areas with a high concentration of patients. Further, if the presence of the virus has been confirmed, a separate screening should be performed for the presence of a chronic infection. Clinical guidelines for hepatitis C include a special test for alcohol consumption by people with HCV. The results of the test are accompanied by behavioral therapy aimed at reducing the amount of alcoholic beverages consumed. This is important because alcohol, combined with the progressive effects of hepatitis, severely destroys the liver.
These consequences include fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver. One of the key recommendations is to assess their neglect. In areas where there is a shortage of medical resources, it is proposed to conduct such low-cost types of testing as FIB4 or APRI. As for hepatitis C and clinical recommendations for its treatment, the latter should be based on the use of antiviral drugs instead of those based on interferon. However, not all PDPs are recommended. For example, Telaprevir and Boceprevir, which were featured in the 2014 WHO reports as effective drugs, have now dropped out of this list. It was proved that the harm from their use exceeds the benefits received.
Disease prevention
It is immediately worth noting that this type of hepatitis C prevention, such as vaccination, does not currently exist. As of 2016, there are several vaccine prototypes in the world that promise to be successful, but so far they are only at the development stage. Therefore, the most important task of prevention is to minimize the risk of HCV infection in those social groups that most often suffer from hepatitis virus. These are for the most part people who are addicted to injecting drugs, as well as people leading a loose lifestyle and not having a permanent sexual partner. In total, HCV prevention is divided into 3 types: primary, secondary and tertiary.
In most cases, the hepatitis virus is transmitted through the blood, so the primary prevention is to use sterile syringes and injection needles, both medical and narcotic. Moreover, the equipment should be exclusively disposable. You can get infected in hospital conditions, in medical institutions. For example, a blood transfusion containing HCV. These cases, however, have become rare, as each donor is tested for hepatitis C before donating blood. In the framework of primary prevention, personal hygiene, such as clean hands, is extremely important.
As for its secondary and tertiary varieties, they are aimed at those people who are already infected with HCV. First of all, it is holding regular consultations regarding possible medical care options. This is a constant monitoring of the liver, whose task is to assess the degree of damage to this organ. An extremely important principle in the framework of secondary and tertiary prevention is to prevent the development of co-infection in the body in the form of joining the hepatitis C clinic to the symptoms of its varieties A and B.
WHO actions and plans
The tasks that WHO sets itself are much larger than simply indicating preventative measures. In 2016, the organization published a multilateral strategy to combat viral hepatitis. It is designed for 5 years and sets itself the task, first of all, of coordinating the efforts of all states and international health organizations to combat the spread of hepatitis. In the future, it is planned to reduce the mortality rate from hepatitis C by 65% by 2030. It is also planned to tightly intersect new cases of HCV infection by as much as 90%, which ideally should exclude hepatitis from the list of international health problems.

Already, the World Health Organization is providing all kinds of support to countries interested in eradicating a dangerous disease. First, WHO uses its resources to screen and treat people with HCV. The organization also provides resources for diagnostic procedures, such as PCR for hepatitis C. WHO also provides statistical reports. Their essence lies in compiling information regarding the spread of hepatitis and the effectiveness of the fight against it. Indicators of mortality, the incidence of a chronic form of the disease and the appearance of life-threatening complications are also noted.
Social and financial aspects of the disease
Due to the fact that most of the society does not have a clear idea of hepatitis, the patients themselves as a result suffer not only from the hepatitis C clinic, but also from the attitude of the surrounding society, which is often biased. Patients are often subject to social exclusion. They are faced with the problem of the impossibility of finding a job, establishing new friendships and love affairs, creating a full-fledged family. As a result, the social adaptation of patients is at stake, which negatively affects their mental health and psychological well-being.
It is also worth noting the price issue. Implementing a full 12-week treatment for hepatitis costs a lot of money due to the high cost of antiviral drugs. And it is considered especially expensive in the CIS countries. For example, in Russia, the treatment of hepatitis C, which uses interferon-free drugs, can reach 1 million rubles. The lack of a unified state policy aimed at combating the inaccessibility of treatment for the general public is slowing down the solution to this issue. State support is limited to conducting medical propaganda, including the creation of Internet sites and platforms, as well as public thematic associations.
The most effective way to combat the high cost of treatment was to introduce generics into circulation - copies of real drugs that have the same features as the original, but are several times cheaper. They are available, however, only in those regions of the world that are recognized by the international community as extremely poor. Patents for the sale of generics in 2013 received Egypt and India.
From there, generics through private individuals get to other countries, in particular, to the Russian Federation. They are prohibited for sale in Russia, but sales are still carried out. There is no other way out for patients - only 10 thousand infected can be treated according to quotas at the expense of the state. The rest are bought by Egyptian and Indian degenerics. In Russia, the price of a drug for hepatitis C, or rather, for its analogue, ranges from 20 to 70 thousand rubles.
General conclusion
Hepatitis C is an extremely dangerous viral disease. He not only can hide himself in the guise of other diseases, but he rarely speaks of his presence. Often, people accidentally learn that they are infected with HCV. This can happen both six months after the virus enters the bloodstream, and several decades later. You can find out about the presence of the virus in the blood using the rapid test for hepatitis C. Prices for it start at 250 rubles and cost no more than 3 thousand. Human immunity has the power to defeat the virus, either by itself or with the help of antiviral drugs used in the acute form of the disease.
If this does not happen, then hepatitis C goes into the chronic stage. It is she who is extremely dangerous for human life, since at this time the risks of developing serious liver lesions increase significantly. For example, fibrosis, cirrhosis, cancer. Therefore, the detection of hepatitis C in the early stages is one of the important diagnostic tasks. If the results of examinations, including PCR for hepatitis C, showed a positive result, then treatment should begin immediately. On average, it lasts 12 weeks and, thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, 95% of patients who have received qualified help eventually recover.
One of the key challenges in the fight against hepatitis C is the high cost of treatment. It costs a lot. In this situation, the poor are saved by generics - effective copies of drugs. The price of hepatitis C medicine in Russia varies from 20 to 70 thousand rubles. Moreover, providing assistance to an individual is not enough, since the world needs a broader coverage of the problems of hepatitis C. Medical propaganda is being actively conducted in this direction, the World Health Organization plays an important role in this.