Gastroduodenitis, the signs of which are found in both children and adults, is an inflammatory disease. A distinctive feature of this pathology is that it affects both the mucosa of the duodenum and stomach. Moreover, the development of the disease begins with the latter. Against the background of the disease, a failure of the autonomic nervous system develops, which regulates gastrointestinal motility. As a result, the smooth muscle mobility fails, and the food lump is delayed in the intestines. An ailment can also occur in a practically healthy individual. After a course of treatment, relapses are not excluded. In this case, chronic pathology in the acute stage is recorded.
general information
Simultaneous damage to the mucous membranes of the initial section of the jejunum and stomach is called gastroduodenitis, so it is difficult and requires long-term therapy. The appearance of this pathology is influenced by both external and internal factors. In addition, heredity plays an important role. Among the psychogenic causes that contribute to its development, frequent stresses and nervousness are distinguished. They produce a negative effect on the general condition of the digestive tract throughout its entire length, i.e., starting from the oral cavity and ending with the act of defecation. Errors in nutrition, including the use of low-quality products, dry food also negatively affects the digestive tract and is one of the reasons for the development of gastroduodenitis.
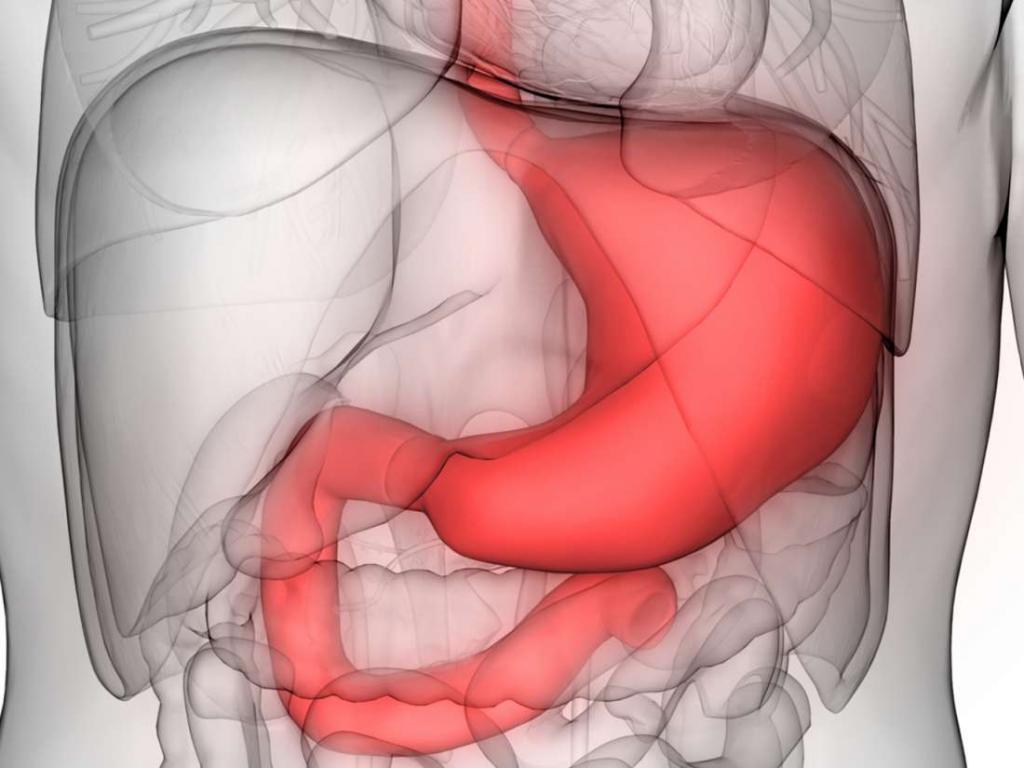
Another provocateur is Helicobacter pylori, which, once in the body, multiplies in the mucous membranes and disrupts their functions. As a result, ulcers and erosion form on it, and due to the aggressive effects of digestive juice, the inflammatory process is aggravated. Gastroduodenitis without signs of mucosal atrophy, what is it? So called some types of disease. In practice, its most common chronic form is preceded by an acute one. And the reason for this phenomenon is the lack or poor quality treatment. In addition, primary chronic gastroduodenitis is no exception. In this case, exacerbations alternate with remission. The complications that most often arise are pancreatitis, enterocolitis, dysbiosis, diarrhea.
Classification of gastroduodenitis
Depending on the reason, it happens:
- exogenous (primary);
- endogenous (secondary) or concomitant.
According to histological indicators of lesion:
- mild;
- moderate
- heavy;
- with atrophy;
- with gastric metaplasia.
According to the localization of pathology:
- chronic ulcer-like;
- chronic gastritis-like;
- local pancreatitis-like.
With the flow:
By prevalence:
From the level of acidity:
Types of disease
Depending on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, the following types are found:
- Superficial - gastroduodenitis without signs, that is, there are no deep damage and erosion, the level of acidity is within normal limits. This type may be as the initial stage of another pathology or as an independent disease. The walls of the digestive organs thicken, swelling appears, the mucous membranes become reddish in color - such changes occur during the development of the inflammatory process.
- Hemorrhagic - there are bleeding erosion on the walls of the mucosa. Permanent blood loss leads to a decrease in hemoglobin concentration, which provokes general weakness. Possible vomiting.
- Mixed - Helicobacter is considered the main cause of this type of pathology. The clinical picture combines the signs of gastroduodenitis of various species.
- Atrophic - precancerous condition. A fairly common form. Due to the severe damage to the membrane that produces mucus, there is a malfunction in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid, which leads to a significant decrease in acidity. Part of the digestive system completely dies.
- Hypertrophic - in addition to thickening, growths and cysts appear on the walls, deep layers of the mucosa are affected. This form is considered the most dangerous, and in the absence of proper treatment, degenerates into cancer.
- Catarrhal is a type of acute pathology, the provocateur of which is an infection of a viral nature.
- Erosive - gastroduodenitis without signs of atrophy, developing rapidly. A stimulating factor is any stressful situation. With an exacerbation of the individual, heartburn, constipation or diarrhea, increased gas formation, belching worries. During remission, all symptoms disappear. With adequate therapy, the disease is completely cured.
- Reflux - bile and food coma are thrown back into the stomach due to a malfunction of the sphincter, which is located on the border of the lower stomach and duodenal ulcer. Such violations in some cases provoke tissue necrosis. In the future, these areas are reborn, and cancer develops.
Clinical picture
Signs of gastroduodenitis in adults in the acute stage are manifested by acid belching, nausea, stomach pain, heartburn, and vomiting. Its duration is several weeks, and then the disease goes into remission, in which symptoms are not observed. However, an individual may experience irritability, dizziness, and general weakness. For incomplete remission, the following picture is characteristic:
- Dyspeptic symptoms.
- Pain of aching character.
- In the language of white plaque.
- After vomiting comes some relief.
- Feeling of heaviness.
- Discomfort after eating.
These are the episodic signs of gastroduodenitis.
Symptoms in children are similar to those in adults, but less pronounced. Among them:
- fast fatiguability;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- in the abdomen, cramping pain;
- increased sweat separation;
- irritability;
- sleep disturbance.
Exacerbation most often occurs in the autumn and spring.
What symptoms indicate a disease?
Gastroduodenitis refers to such ailments that should be treated quickly, otherwise they will rapidly progress. Signs that indicate pathology appear in individuals in different ways. They are most noticeable during the period of exacerbation, when a person is concerned about pains such as spasm and bloating. Indirect signs of gastroduodenitis include:
- Loss of appetite - if it is absent for a long period, then an examination is required, which the doctor will prescribe when contacting a health care institution.
- Weight loss - not every patient is found. Uncontrolled weight loss is an alarm that requires medical attention.
- Weakness - this symptom manifests as the disease progresses. If unreasonable fatigue or lethargy does not go away within two weeks, then the help of doctors is required.
Unfortunately, adults often do not pay attention to the above signs of gastroduodenitis. Nevertheless, indirect symptoms not only signal emerging health problems, but also help prevent serious complications.
Treatment
Depending on the type of pathological process, the doctor selects complex therapy for:
- Superficial - medicines that regulate the level of acidity, immunomodulators, physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapeutic treatment, diet food.
- Erosive - sedatives, painkillers, vitamins, antibiotics, cytoprotectors.
In case of severe gastroduodenitis, its treatment is carried out in a hospital. In the acute state, a complete cure occurs after a single drug course and diet. If there are repeated episodes of the disease, then a full treatment and observation by a doctor is necessary. To prevent relapse, it is recommended to completely abandon strong coffee and any alcohol-containing, carbonated drinks.
Diet food
In the treatment of signs of gastroduodenitis, diet is important. During exacerbations, it is advisable to follow the following rules:
- All food should be warm. They cook steamed dishes, boil or stew. They eat in small portions, observing equal intervals between meals (at least three hours). Dinner no later than two hours before bedtime.
- It is allowed to drink weak tea drinks, any sour-milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables. Cooked sausages and cheeses are allowed in small quantities.
Forbidden to use:
- Tasteful foods.
- Rough and fried foods.
- Chocolate.
- Pickles, canned food.
- Mushrooms.
- Coffee and alcohol drinks.
As a prevention of the development of signs of gastroduodenitis with the existing form of chronic gastritis, doctors recommend that you adhere to the daily routine and follow a diet. It is based on the following principles:
- A varied menu throughout the day.
- Eating at least four times a day.
- Exclude food in the dryer, overeating, long breaks between meals.
Adhering to the above principles of nutrition is also recommended in the initial stages of the disease.
Features of superficial gastroduodenitis
With this form of the disease, only the surface layer of the mucous membrane is affected. There are several types:
- Erythematous is the initial form of the disease in which the symptoms of superficial gastroduodenitis are poorly expressed. The main symptom is a decrease in appetite, and discomfort after eating.
- Acute - exacerbation of the previous form.
- Chronic - occurs with untimely and incorrect treatment.
Often superficial gastroduodenitis passes to the upper parts of the duodenum, since there is no muscle sphincter between the intestine and stomach.
Signs of gastroduodenitis depend on the age, form and course of the disease:
- Dyspeptic phenomena. Violation of the motility of the duodenum and stomach is considered the main symptom of the disease. In addition, the individual has nausea, urge to vomit, heartburn, bloating, heaviness in the stomach. In some cases, there is bitterness in the oral cavity.
- Pain syndrome. Its appearance depends on the meal, often there are so-called “hungry” pains in the early morning hours, and can also be in the evening, two or three hours after dinner. In the period of exacerbation, the pain is localized in the left hypochondrium.
- Headache, fatigue, weakness. Such signs are most often characteristic of children and adolescents. Often they are joined by increased saliva, constipation or diarrhea, lack of appetite, weight loss.
Symptoms of the pathology in the acute stage are worried for three months. The pain syndrome is episodic and is short-lived. If untreated, signs of chronic gastroduodenitis develop in adults and children. This form is characterized by cyclicality, i.e., periods of exacerbations are replaced by prolonged remissions.
Causes of Chronic Gastroduodenitis
Allocate endogenous and exogenous causes that provoke the onset of the disease. The first include:
- Anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract, among which there is a hormonal malfunction in the regulation of digestion, a decrease in the secretion of mucus necessary for digesting food, and increased acidity.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Damage to the pancreas and liver.
Secondary chronic gastroduodenitis develops against the background of pathologies such as renal failure and chronic gastritis, hepatitis, peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, allergic or parasitic diseases, as well as damage to the heart and blood vessels.
Exogenous reasons include:
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- eating large amounts of food, very hot, cold or spicy foods.
The above reasons provoke an increase in the production of hydrochloric acid, reduce the formation of bicarbonates in the pancreas, the failure of the evacuation and motor function of the digestive tube.
In addition, the hereditary factor is not excluded.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum
Signs of chronic gastroduodenitis are found in both children and adults. The clinical picture is as follows:
- bursting and heaviness in the stomach;
- discomfort in the epigastric region, as well as pain, which occurs an hour or a half after eating;
- heartburn;
- vomiting
- acid burping;
- diarrhea alternate with constipation;
- the tongue is covered with a touch of tan;
- it smells unpleasant from the oral cavity;
- excessive sweating;
- the skin is pale;
- irritability;
- sleep disturbance;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- pain on pressing on the epigastric region.
The period of exacerbation, which can take up to two months, and remissions alternate. During the relapse of the individual, pain lasts about ten days. They are also capable of occurring suddenly. The first attack of the disease appears unexpectedly and often on an empty stomach. In this case, the person feels cramping pains in the upper abdomen, to which nausea and vomiting join. In case of incomplete remission, the signs of chronic gastroduodenitis subside.
Therapeutic measures
The treatment of the chronic form is quite lengthy. All patients are required to adhere to a special diet. It is recommended to include grated porridge prepared with mushroom, meat or vegetable broth, any sour-milk products, and bread products with the exception of muffins in the diet. Freshly squeezed juices are allowed. Steamed food, stewed, baked, boiled. Food is taken up to five times a day in small portions in a warm form.
In the acute period, bed rest is necessary for eight days. Dietary nutrition reduces the intensity of pain and inflammation. Due to the fact that Helicobacter is a common cause of infection, one of the following treatment regimens for signs of gastroduodenitis is selected:
- "Metronidazole", bismuth preparations, an antibiotic from the tetracycline group. Course treatment up to two weeks.
- Clarithromycin, Omeprazole, Metronidazole - seven days.
- Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, Omeprazole - from ten to fourteen days.
If there is an increase in acidity, then medicines such as:
- “Cimetidine”, “Famotidine”, “Ranitidine”.
- “Rabeprozole”, “Omeprazole”, “Esomeprazole”, “Lansoprazole”, “Pantoprazole”.
- "Bismuth Sucralfat."
- Antacids.
- Prokinetics.
- Enzymes.
With an exacerbation of chronic pathology, the following pharmacological groups of drugs are shown:
- painkillers;
- enveloping walls of the stomach;
- enzymes;
- antibiotics.
All patients are recommended balneological and sanatorium treatment in the resort area, physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises.
The use of herbal recipes is allowed only after an accurate diagnosis and consultation with the attending physician.
Gastroduodenitis in adolescents: signs, treatment
In the formation of the disease, the main role is given to unbalanced and irregular nutrition, as well as Helicobacter infection. In addition, the likelihood of its occurrence increases with traumatic factors.
Initial diagnosis is difficult, as the clinic resembles gastritis symptoms. Chronic gastroduodenitis is almost always accompanied by duodenal hormonal insufficiency. As a result of a violation of the synthesis of hormonal substances, a malfunction occurs in many organs and systems of the body.
One of the most common signs of gastroduodenitis in adults, as well as a symptom in adolescents, is dull pain, aching in nature. It intensifies at night, and in addition, makes itself felt in the case of a long interval between meals. With gastroduodenitis of giardiasis, acute colic is observed in the navel. Pain in some cases is accompanied by facial flushing, tachycardia and increased sweating.
Unlike children, adolescents are quite often worried about heartburn. Nausea and vomiting that occurs in the early morning hours or after a certain time after a meal are also considered characteristic symptoms of the disease and have a long period. At the same time, drugs with an antiemetic effect do not bring relief. Due to the violation of peristalsis, diarrhea and constipation occur. If the teenager did not eat for a long period, then he begins to have headaches, they are called duodenal migraines. They are accompanied by nausea, dizziness. With gastroduodenitis in the chronic phase, loss of appetite, frequent palpitations, general weakness, pain in the chest area, drowsiness are observed.
Therapeutic measures are as follows:
- With exacerbation of signs of gastroduodenitis, bed rest for eight days. Dietary nutrition. №1, – №5.
- – .
- .
- H2-, «» .
- , , .
- .
- .
- .
The treatment of symptoms in adults and children is slightly different, and the precautionary measures are the same for all ages and genders. They consist in observing a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet, compliance with the regime, moderate physical exertion, proper rest and sleep.
In addition, it is recommended to avoid overstrain, timely treat gastrointestinal diseases. Secondary prophylaxis is aimed at preventing relapse, that is, regular therapeutic courses are indicated during periods that are more likely to develop exacerbations (spring, autumn). During this period, you should adhere to dietary nutrition (table number 5), drink mineral water, engage in physiotherapy exercises, and also undergo a course of physiotherapy treatment so as not to aggravate the existing signs of gastroduodenitis. Symptoms in adults and children for the most part may not bother for a long time, but only under the condition of quality therapy. Otherwise, the course of the disease is severe and leads to a deterioration in the quality of life, and negatively affects the individual's ability to work.