What a blessing for parents when their baby is born healthy. Unfortunately, this is not the case with everyone. There are dozens of birth defects that, from the first minutes of the baby's birth, endanger his life. One of the most severe is bladder exstrophy. According to statistics, it is extremely rare and is recorded in about 1 case per 30 thousand live babies born. This is an average value, because in some areas the number of children with such a defect can rise to 1:10 000 or fall to 1:50 000. But parents who encounter such a problem do not care about statistics, it is important for them to save the life of the child and raise him a full-fledged person. What kind of anomaly is this and what are the chances of having babies born to her?
How is the human urinary system
A better understanding of what is bladder exstrophy will help knowledge of the correct structure of the urinary system. Simplified, it looks like this: urine is excreted from the kidneys during blood filtration, which enters the urinary bladder through the ureters. This is a hollow organ that can stretch, which makes it possible for fluid to accumulate in it to certain limits and only then it can be brought out through the urethra. In the place where this canal begins and the bladder ends, there is a special muscle called the sphincter. Its purpose is to prevent the flow of urine spontaneously. The bladder is located in the lower abdomen, in the pubic region. Like all internal organs, it is covered from the outside world by body tissues, in particular by the anterior wall of the peritoneum. Its own walls consist of several layers - mucous, submucous, muscle, others - and are penetrated by multiple blood vessels that determine its color. The rectum is located in the immediate vicinity of the bladder, but their walls and tissue layer interfere with the mixing of urine and feces.
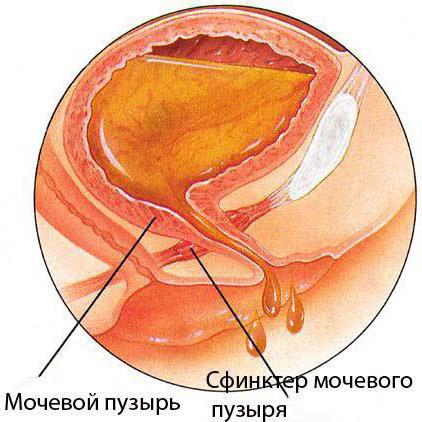
External characteristics of the pathology
Bladder exstrophy is diagnosed with the naked eye from the first moments of a child’s life. With this pathology, there is no section of the peritoneum, that is, there is a hole in the pubic region, the sizes of which can vary from 3 to 12 cm. As a result of such a pathology, the bladder is outside the body. Its front wall is also absent, but the work of the ureters is not impaired. Urine entering them from the kidneys is excreted in drops or trickles into what remains of the bladder, and then through a hole in the peritoneum it comes out. In this case, there is no bleeding, since the edges of the dissections of the walls of the abdomen and bladder are formed and do not have damaged blood arteries. However, the open mucosa is always easily injured, even from the touch of a diaper. Other defects visible to the eye are the location of the navel too low or its complete absence and a higher position of the anus. One of the imperceptible at first glance defects is the discrepancy (rotation) of the pubic bones. From the norm, this indicator can differ significantly (the difference is up to 7 cm), which subsequently greatly changes the gait. Patients who did not correct this deviation on time move around, rolling from side to side (like a duck). Despite the complexity of the pathology, the newborn is quite viable, active and, with proper treatment, has good chances.
Epispadias
This congenital defect can be independent, but very often it is a concomitant additional defect in those who have established bladder exstrophy. Epispadia is a splitting of the wall of the urethra. It can be incomplete (only the tip is split) or total (the urethra is completely split from the outer edge to the bladder). Treatment of this defect is carried out only surgically, and if epispadias is an independent disease, the child is only operated on when he reaches the age of 1-3 years, but in cases where the defect accompanies bladder exstrophy requiring immediate intervention, the operation to eliminate epispadias can be performed in more early dates.
Causes
There is no exact answer to the question of why bladder exstrophy occurs in children. Scientists only managed to find that pathology occurs if, during the formation of organs and tissues (4-5 weeks after conception), embryos suddenly experience a malfunction in cell division and connection. As a result, the cloacal membrane cannot close, and the bladder is outside the body. Why is the process of cell division disturbed? Specialists call the reasons common to all malformations:
- smoking and drinking during pregnancy;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- adrenal hyperplasia;
- side effects of drugs;
- chemical poisoning and others.
By laboratory tests it was established that the appearance of extrophy in experimental animals was greatly influenced by the effects of drugs with cortisone.
Many experts do not exclude the genetic nature of the disease, for example, in parents with bladder exstrophy and in families where there are relatives with this disease (uncles, aunts, nephews), the probability of having a child with the same deviation is 1:70, and in families , where there is already a sick child, 1: 100. But immediately in both twins this defect is rarely observed and almost never if they are identical.
Do I need a diagnosis?
By external signs, any doctor from the first seconds of a baby’s birth can accurately diagnose bladder exstrophy. Photos demonstrating how this defect may look cannot be called pleasant, therefore we do not publish them (schematic images are quite enough). Everything seems to be clear, but a diagnosis in order to identify all possible concomitant deviations is necessary. First, urine should be examined for peritoneal fluid and serous exudate.
It is also necessary to do cystoscopy, ultrasound, tomography and endoscopy. As a rule, genetic studies are also shown to confirm or exclude Down and Edwards syndromes.
Malformations of the urinary system in boys
Relentless statistics say that boys have bladder exstrophy, and with it epispadias, are observed 2-5 times more often than girls. Due to differences in the structure of the genital organs, the congenital pathologies of the urinary system in girls and boys are slightly different. Concomitant diseases in males in childhood can be cryptorchidism, underdevelopment of the testicles, aplasia of the prostate gland, and later Peyronie’s disease (member curvature). Already in infancy, in boys with bladder ostrich, a significant decrease, compared with the norm, of the size of the penis is noticeable, in some cases it may not be at all. This is due to the fact that the pubic bones, turning, as if pull up cavernous bodies, interfering with their connection. If extrophy occurred together with epispadias, boys have a dissection of the glans penis and the location of the anus closer to the scrotum.
Bladder exstrophy in girls
In the fairer sex, this disease is extremely rare. Concomitant defects here may be underdeveloped labia and / or vagina, cleavage of the clitoris, displacement of the anus closer to the vagina, up to 1.5 cm lower position of the cervix (in some cases it is clearly visible). In general, in children of both sexes, there is a decrease in the volume of the bladder, lack of sphincter, improper location of the ureters, problems with the kidneys, liver, spleen, and genetic abnormalities are possible.
Urinary care for newborns
There are 3 degrees of bladder exstrophy:
1. A hole in the peritoneum is up to 4 cm, there are no concomitant defects.
2. The divergence of the tissues of the peritoneum and pubic bones up to 5-6 cm, there are 1-2 concomitant defects.
3. Several severe concomitant defects (total epispadias, cystic extrophy and others), discrepancy of the peritoneum and pubic bones from 8 cm.
With any degree of deformation, the child’s urine is constantly poured onto the mucous membranes, which causes their inflammation, up to peritonitis and pyelonephritis. Mucous membranes also suffer from the touch of a diaper, napkins, other coating materials, and from hypothermia, and from the loss of moisture by the mucous membranes. Therefore, bladder exstrophy in newborns requires maximum sterility and the creation of acceptable environmental conditions. In order to avoid infections, babies are urgently given courses of antibacterial therapy and, if possible, they are placed in piles (small boxes).
Constantly pouring urine can lead to dermatitis, as well as provoke papilloma growths that form already at 3-4 weeks of a baby's life.
Another bad symptom: due to irritation of the mucous membranes and extreme discomfort, the child refuses to eat, sleeps poorly and, as a result, lags behind in development.
Treatment
Only surgically at this stage in the development of medicine is bladder exstrophy treated. Total epispadias, if it accompanies the above-mentioned anomaly, significantly complicates the already difficult and life-threatening intervention of the baby. Operations are usually carried out a lot. The first, according to most doctors in the world, should be done almost immediately after birth, at the age of a child 1-10 days. Its goal is to create the front wall of the bladder from existing tissues and close it, create a sphincter, reduce the frontal bones, if there is enough skin, close the gap in the peritoneum. If the hole is too large and the baby does not have enough tissue to close it, it is possible to use an artificial film, which is subsequently removed. After this operation, the risk of infection of the genitourinary organs disappears, but urinary incontinence persists .
The second operation is done when the child reaches the age of 1 year, but no later than 2 years. It lies in the genital plastic. In girls, if there are no contraindications, it can be performed during the first intervention. In some clinics, with repeated surgery, the ureters are transplanted into the sigmoid colon and create an antireflux mechanism to rid the child of urinary incontinence.
The third surgery is performed when the child reaches the age of 5 years. At this stage, the neck of the bladder, sphincter are formed, other actions are performed that contribute to the retention of urine (if this has not been achieved before) and the correct development of the genitourinary organs.
The following operations are performed according to indications. In particular, procedures to restore urine retention in girls are performed even at 16 years old, and in boys - from 17 to 18 years old.
Adult bladder exstrophy
Since in the vast majority of cases this pathology is corrected in childhood, adults with bladder exstrophy are rare. This happens in cases where the baby, for many reasons, did not undergo surgery on time, or they were performed with errors. People with this defect have difficulty social adaptation in the team due to urinary incontinence. This problem is considered one of the most important. Recently, several methods have been known for performing operations to eliminate it, but with any of them, adult bladder exstrophy is successfully cured only in 40-80 percent. The photo below shows the preparatory phase before the operation.
The second important aspect of the problem is the sexual adaptation of adults, especially men born with bladder exstrophy. Despite all the efforts of doctors, it is impossible to achieve a complete restoration of the cavernous bodies of the genital organs of men. Firstly, because they are almost always deformed, and secondly, because their volume is simply not enough, even when cutting them from the pubic bone. Therefore, the maximum length of the penis almost never exceeds 6-7 cm, although the erection is not broken. Patients undergo urogenital plastic surgery, in addition, psychotherapy sessions and drug treatment are indicated.
Prevention
Since the exact causes of the pathology we are considering are unknown, doctors today cannot fully answer the question of why bladder exstrophy occurs. Prevention is to abstain from smoking, drugs, alcohol. You should also be tested for the presence of herpes viruses, rubella, syphilis, toxoplasmosis and other embryotoxic infections. Genetic consultation also plays an important role, especially if the family already has patients with estrophy or epispadias of the bladder. This deviation shows ultrasound, which gives the woman the right to decide whether to leave her a sick child or not.
People born with this pathology should be monitored by a urologist all their lives. Of great importance for them is the observance of a diet that excludes all salty, spicy, peppered, alcohol and the use of large volumes of liquid.