Phlegmon is a purulent inflammation of adipose tissue. The pathological process is acute and in a short time can cover the tissue surrounding the area of inflammation and spread to tendons, muscles, and cell spaces. In this article we will talk more about this disease, the symptoms, causes and treatment principles of this disease will be described below.
Causes
First of all, the concepts of “abscess” and “phlegmon” should be clearly separated. This is not the same thing. Unlike an abscess, which has a restrictive capsule, phlegmon does not have clear boundaries, so the inflammatory process is diffuse. Phlegmon is a disease that develops as a result of rapid proliferation of pathogens: staphylococcus, streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, clostridia, Escherichia coli, etc.
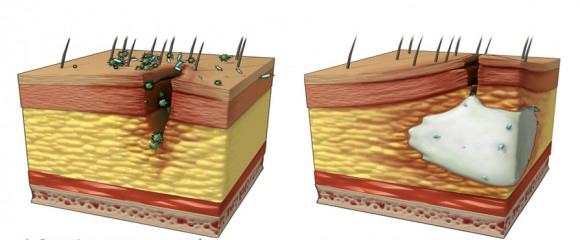
Malicious organisms can penetrate into fatty tissue in various ways. Most often this occurs as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin during wounds, trauma, after surgery and injections. Also, the infection can get with the flow of lymph or blood. A contact path of infection is also possible if the purulent focus from the affected organ breaks into adjacent adipose tissue. A certain danger is posed by a running limited process (carbuncle, abscess). The body, as a rule, seeks to limit any developing inflammation by forming a capsule. However, with depletion, decreased immunity, prolonged chronic pathologies, alcoholism, such a protective capsule does not form, and the purulent process spreads unhindered from the very beginning of the disease. In addition, some pathogens (for example, non-clostridial flora, clostridia) can secrete special substances that dissolve the protective membrane, as a result of which pus can also penetrate into healthy tissues.
Phlegmon: symptoms of the disease
The disease is characterized by fairly typical external manifestations, similar to signs of an inflammatory process: redness, swelling of the skin, warming of the skin at the site of the lesion, pain.
By the nature of the location, phlegmon can be superficial (tissue damage to the muscle layer) and deep (damage to the muscle layer and fatty tissue located around the internal organs). Superficial phlegmon is manifested by intense pain in the area of inflammation, swelling, and compaction. When the skin is involved in the pathological process, redness and a local increase in temperature develop. Very soon, general symptoms of intoxication are observed : chills, fever, thirst, dry mouth, marked general weakness. If deep phlegmon develops, general symptoms prevail over local ones. Body temperature may rise to 40-42 ° C, headaches, lethargy, drowsiness appear, skin integuments become icteric, blood pressure decreases, pulse is weak, frequent. The respiratory activity is disturbed (breathing goes astray, shortness of breath occurs with slight physical exertion or even at rest) and excretory (the amount of urine decreases, up to its complete absence) systems. Also, with deep phlegmon, this or that region increases in size in comparison with a healthy symmetrical site.
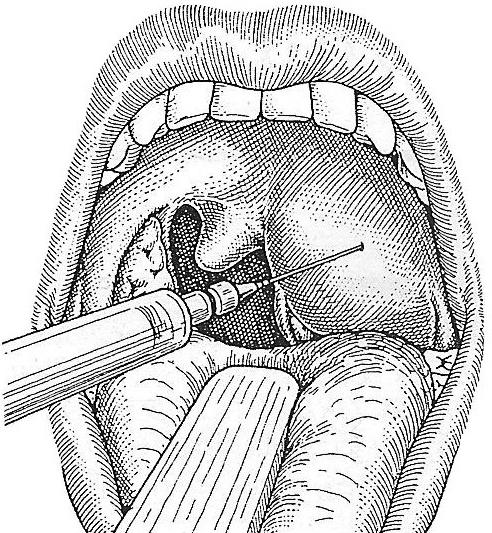
Phlegmon neck
This ailment can develop in absolutely any area where there is subcutaneous fat. Phlegmon of the neck is a disease whose course is unpredictable. And the consequences can be severe and even pose a threat to life.
With the disease, interfascial and intercellular spaces of the neck are affected. Since this part of the body has a complex anatomical structure, the phlegmon can have different localization.
Symptoms of phlegmon neck
It is very important to diagnose the disease on time. Phlegmon can manifest itself in different ways, it all depends on the depth and location. If the inflammation is small and deep, it is difficult to detect. In this case, there are no manifestations on the skin, the body temperature does not rise to high values, signs of intoxication are weak. External or extensive phlegmon of the neck manifests itself in the same way as superficial phlegmon of other parts of the body. On palpation, fluctuation (accumulation of fluid), tension of the skin and severe soreness will be felt. The patient's condition is moderate or severe. With this kind of pathology, swallowing can be difficult. With submandibular phlegmon, difficulties arise with opening the mouth and chewing food. The mouth is always in an ajar state, an unpleasant odor can often be observed. With a progressing pathological process, the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates, manifestations of intoxication increase. Blood tests show a picture of acute inflammation, ESR levels increase to 40-50 mm / hour.

What causes phlegmon neck?
Phlegmon is an inflammation in which pus spreads very quickly from one space to another, while forming spilled vast areas of damage. In particular, neck phlegmon can be provoked by a complicated course of catarrhal and lacunar angina, opening of peritonsillar and pharyngeal abscesses, alveolitis, periodontitis, osteomyelitis of the lower jaw, otitis media, damage to the spine (osteomyelitis of the occipital bone or cervical vertebrae), thyroid gland disease, ), injuries. The causative agent of infection spreads very easily through loose interfascial fiber, affects the connective tissue, blood vessels, muscles, as well as lymph nodes.
Possible complications
Incorrect and untimely diagnosis of the disease can lead to serious consequences, often incompatible with life:
inflammation of the middle space of the chest - mediastinitis;
to pus erosion of the walls of blood vessels and, as a result, to profuse bleeding ;
to meningitis, sepsis, abscess in other organs;
to asphyxia (as a result of pus compression of the respiratory tract);
to breaking pus into the lungs, larynx.
Phlegmon: treatment of the disease
First of all, to confirm the infectious nature of inflammation, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination of the patient and study the medical history. Phlegmon is usually removed surgically. The use of antibiotic therapy, novocaine blockade, physiotherapeutic treatment, the introduction of medications that strengthen the body's defenses, is possible only at the initial stage of the disease. If the quick positive effect does not occur (the pain does not stop, the body temperature is kept at a high level, overall health and blood counts do not improve), and the symptoms of intoxication are rapidly increasing, emergency surgery is necessary. Surgical manipulations in the early stages of the disease can prevent poisoning of the body and the spread of purulent process. During surgical treatment, it should be borne in mind that neck phlegmon, for the most part, are located subfascial, and in order not to damage important formations (nerves, blood vessels, etc.), it is necessary to carefully dissect the tissue layer by layer.
However, the therapy does not end there. After the phlegmon is removed, treatment in the postoperative period involves active therapeutic action. Drainages are introduced into the wound so that prolonged flow washing and active aspiration of the exudate are possible. Also, the patient needs to provide bed rest and plenty of water. In high doses, physiological saline, glucose, etc. are administered. The use of antibiotics, painkillers, cardiac drugs, and oxygen therapy is indicated.
Preventative measures
To prevent such a dangerous disease, it is necessary to avoid microtraumas in everyday life and at work, to immediately provide medical care for injuries, injuries, the introduction of foreign bodies. Preventive measures for phlegmon of the neck include timely treatment of tonsillitis and regular visits to the dentist in order to identify and treat diseases of the teeth and gums in time.
Finally
Phlegmon is a severe, life-threatening inflammation. At the first manifestations of the pathology, consult a doctor immediately. Do not self-medicate in any case, this can lead to irreversible consequences.